Overview
Lake Superior's average depth of approximately 483 feet profoundly influences its ecological dynamics, thermal stratification, and overall water quality, establishing it as the deepest of the Great Lakes. The average depth of Lake Superior helps explain why its waters stay colder, clearer, and less biologically productive than shallower lakes. The average depth of Lake Superior helps explain why its waters stay colder, clearer, and less biologically productive than shallower lakes. This remarkable depth not only supports diverse aquatic ecosystems by regulating temperature and nutrient distribution but also plays a critical role in maintaining the lake's clarity and low pollution levels. Such characteristics underscore its vital importance as a natural resource.
Introduction
Lake Superior, the largest freshwater lake by surface area, commands attention not only for its vastness but also for its extraordinary average depth of approximately 483 feet. Its surface area of Lake Superior and its immense volume combine to shape weather, shoreline conditions, and the scale of ecological processes. This remarkable depth plays a crucial role in influencing the lake's ecological balance, climate regulation, and biodiversity, establishing it as a compelling subject of study.
As we explore the intricacies of Lake Superior's depth, it prompts critical questions about its impact on the surrounding environment and the unique challenges it presents. Understanding the depth of Lake Superior is essential for linking physical measurements to real environmental outcomes.
- How does this profound measurement affect the lake's ecosystems and the communities that rely on its resources? Because the lake superior depth in feet varies dramatically across locations, conditions near shore can differ greatly from offshore waters.
- Delving into these dynamics reveals the lake's true significance, extending far beyond its mere physical dimensions.
Define Lake Superior's Average Depth
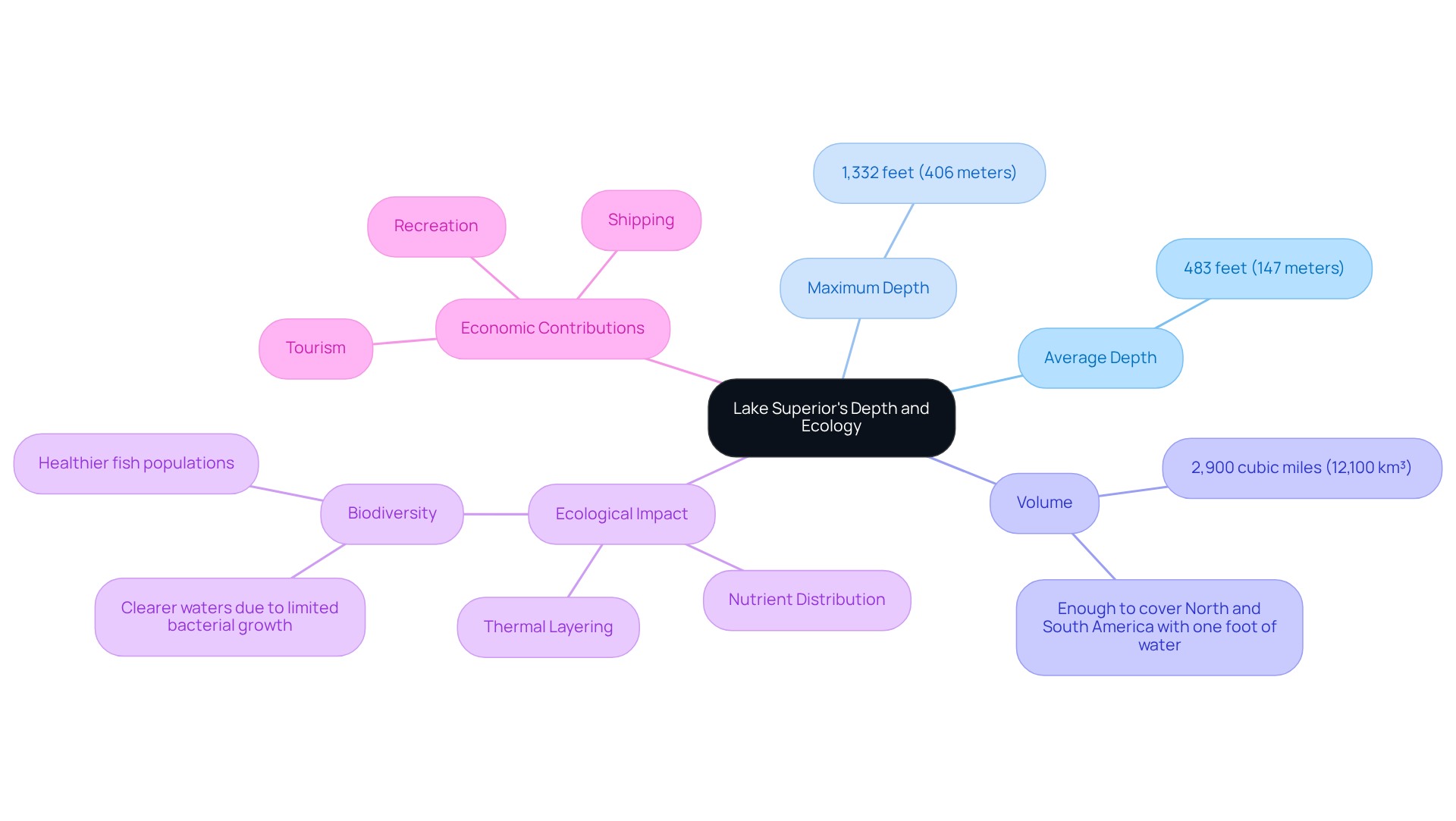
Lake Superior's average depth, known as the most profound of the Great Lakes, is approximately 483 feet (147 meters). Its maximum depth reaches an impressive 1,332 feet (406 meters), a factor that significantly influences the lake's ecological and hydrological dynamics. The maximum depth of Lake Superior is often used to describe why its deepest basins behave more like an inland sea. This extraordinary depth enables Lake Superior to hold around 2,900 cubic miles (12,100 km³) of water—enough to inundate both North and South America with one foot of water. Such a vast volume plays a crucial role in regulating local climate conditions and supporting diverse aquatic ecosystems.
The lake's profundity contributes to its unique thermal layering, impacting nutrient distribution and the overall well-being of its biological communities. The deepest part of lake superior stays intensely cold, shaping oxygen patterns and limiting decomposition compared with warmer, shallower waters. For instance, the cold temperatures at greater depths create a habitat that limits bacterial growth, resulting in clearer waters and healthier fish populations. Moreover, this largest freshwater body is often misrepresented as merely a body of water; it resembles an ocean, as noted by George Grant, who remarked that those who have never observed it possess a limited understanding when referring to it as just a body of water.
Understanding these measurements is vital for grasping the significant role of Lake Superior, especially considering the Lake Superior average depth, in regional ecology and climate, underscoring its value as a natural asset and a distinct environmental entity. Locating Lake Superior's deepest point helps scientists track circulation, habitat zones, and how conditions change from top to bottom. Furthermore, the lake's biodiversity is essential for maintaining healthy ecosystems, and its economic contributions through shipping, tourism, and recreation highlight its significance beyond mere ecological metrics.
Contextualize Lake Superior's Depth in the Great Lakes
The largest by surface area among the Great Lakes—Michigan, Huron, Erie, and Ontario—not only holds the title of the most expansive but also that of the deepest. In the Great Lakes of America, Lake Superior’s depth is a defining feature that shapes conditions across the entire basin. With a mean depth of 483 feet, it surpasses the Lake Superior average depth compared to Michigan's waters at 279 feet and Huron's waters at 195 feet. The greatest extent of this largest freshwater body in North America reaches an astonishing 1,332 feet, with an overall volume of approximately 12,088 cubic kilometers. This considerable volume contributes to the colder temperatures and distinct ecological conditions of the largest freshwater lake, establishing it as an essential habitat for diverse species and a vital resource for nearby communities. The lake's measurements also influence its water retention duration, estimated at around 191 years, which plays a critical role in its water quality and ecosystem health.
Furthermore, this largest freshwater lake is recognized for its comparatively low pollution levels, enhancing its biodiversity and ecological balance. Since Lake Superior freshwater is a common lake, its low pollution profile helps explain why it remains a prized water resource. Case studies highlight that the ecological dynamics of this vast body of water are closely tied to its measurements; for instance, its immense volume helps in reducing pollution, placing it among the least contaminated lakes in the region.
In summary, the profundity of Lake Superior, specifically its average depth, is not merely a physical characteristic; it is a crucial element that defines its ecological identity, impacting temperature, water quality, and the overall well-being of its ecosystem. Understanding the deepest point in the Great Lakes clarifies why Lake Superior’s conditions differ so sharply from the other lakes.
Examine the Geological Formation of Lake Superior
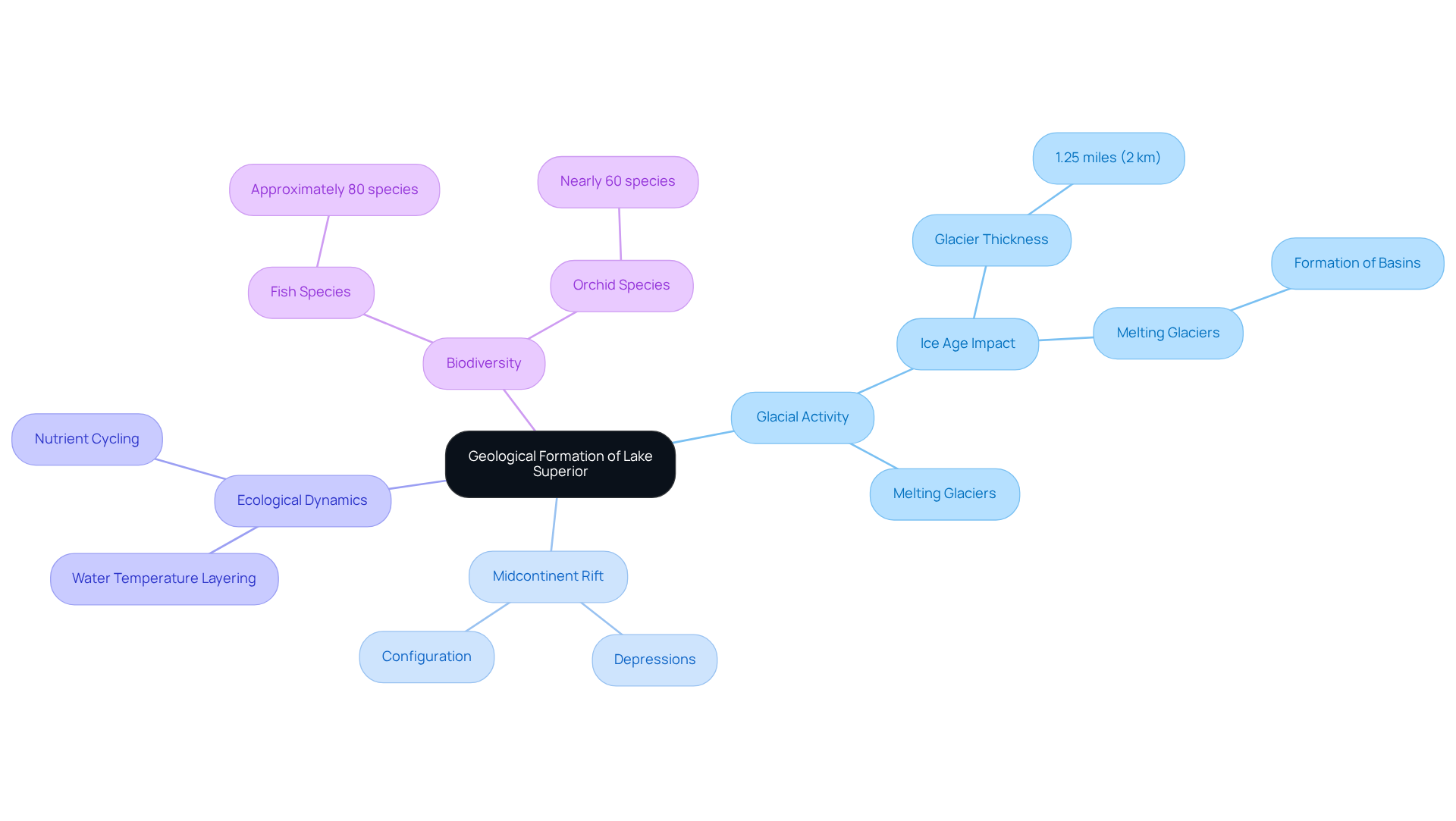
The formation of this expansive body of water stands as a remarkable testament to the formidable power of glacial activity, tracing back approximately 10,000 years. The scale of the Great Lakes of America is rooted in processes like these, where ice and geology worked together over vast time spans. During the last Ice Age, colossal glaciers advanced and retreated, meticulously sculpting the basin that now contains this vast expanse of water. The Midcontinent Rift, a geological formation that began developing over a billion years ago, has significantly shaped the magnitude and configuration of this water body. This rift created a series of depressions that filled with water as the glaciers melted, leading to the Lake Superior's average depth of 1,333 feet (400 meters). Knowing what the deepest point of lake superior helps explain why some basins behave like deep, cold reservoirs. The ice thickness during the Wisconsin glaciation reached an astounding 1.25 miles (2 km), underscoring the profound impact of glacial activity on the formation of this body of water.
The intricate interplay between glacial activity and geological processes has not only defined the physical characteristics of the body but also significantly influences its ecological dynamics. In large systems like Superior Lake, depth-driven layering can shape everything from oxygen levels to habitat boundaries. For instance, the Lake Superior average depth of the largest freshwater body contributes to water temperature layering, which in turn affects the distribution of aquatic organisms and nutrient cycling within the water. Lake Superior is home to approximately 80 species of fish, showcasing the ecological diversity that arises from its unique geological characteristics. Moreover, the body of water boasts an average underwater visibility of 27 feet (8.2 meters), highlighting the clarity of its waters, a vital aspect of its ecological dynamics. Case studies illustrate how these glacial formations have fostered diverse habitats, supporting nearly 60 species of orchids in the surrounding basin. Understanding this geological history is essential for appreciating the area's current ecological significance and the ongoing conservation initiatives aimed at safeguarding its distinctive environment.
Outline Key Characteristics of Lake Superior's Depth
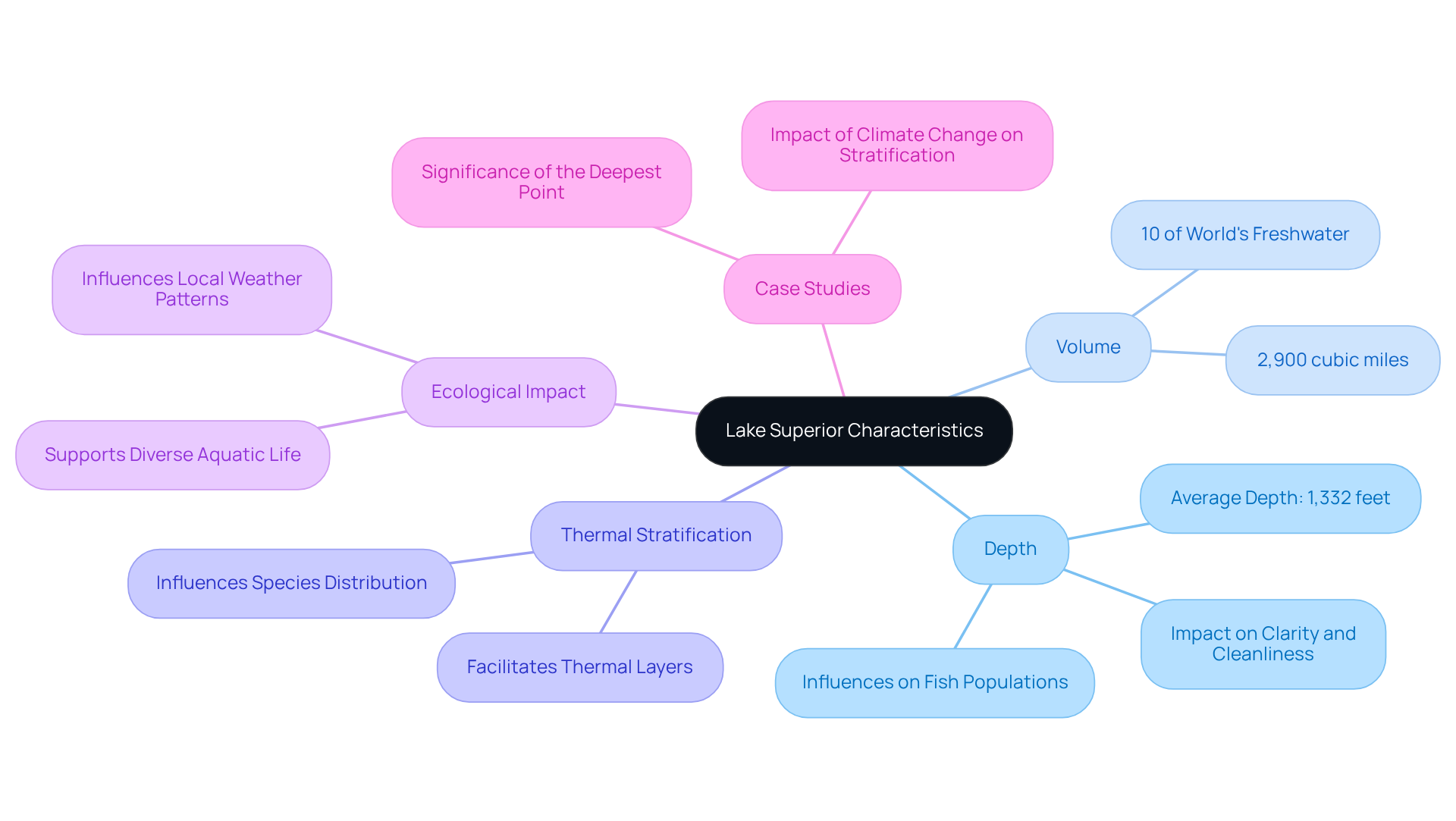
Lake Superior's extraordinary measurements play a pivotal role in shaping its ecosystem. When people ask how deep Lake Superior is, they are often trying to understand the ecological effects of these measurements. This remarkable body of water, with a Lake Superior average depth of 1,332 feet, holds a staggering volume of 2,900 cubic miles, facilitating thermal stratification—a phenomenon where warmer water layers float above colder ones. Such layering is crucial for species like trout, which favor the cooler, deeper waters. The deepest part of Lake Superior maintains colder conditions that persist even during warm months, strengthening these habitat patterns. Furthermore, this profundity enhances the lake's clarity and cleanliness, as deeper waters typically exhibit lower nutrient concentrations, thereby reducing the frequency of harmful algal blooms. Notably, this largest of the Great Lakes contains 10 percent of the world's accessible surface freshwater, underscoring its global importance.
The level of Lake Superior significantly influences local weather patterns, contributing to unique phenomena such as lake-effect snow, which can dramatically impact surrounding areas. Since Lake Superior is a freshwater is commonly asked, its freshwater status also shapes ice formation, evaporation, and seasonal weather effects. Research indicates that the lake's measurements are essential for maintaining ecological balance, supporting diverse aquatic life and influencing their distribution. For instance, studies have shown that the extent of the lake affects fish populations, with species richness varying based on thermal layers and nutrient availability.
Additionally, the ecological interactions of this great lake are further illustrated by case studies emphasizing the connection between water level and aquatic life. The case study titled 'Significance of the Deepest Point' highlights how the Lake Superior average depth influences ecological dynamics and conservation efforts. The phrase deepest point in the great lakes is often used here because Lake Superior sets the benchmark for depth-related ecosystem behavior. Moreover, the observed thermal stratification in the lake has been linked to variations in fish populations, with certain species thriving in specific thermal layers. As Dan Bevilacqua noted, understanding the lake superior average depth and ecological significance of Lake Superior is crucial for promoting and conserving this remarkable natural resource. Recognizing these interactions is vital for conservation efforts and resource management, ensuring the health of this significant freshwater resource.
Conclusion
The significance of Lake Superior's average depth extends far beyond mere measurements; it serves as a critical element shaping the lake's ecological identity and its role within the Great Lakes system. Placing it on the great lakes in north america map helps visualize why its size and depth dominate regional freshwater dynamics. With an average depth of 483 feet and a maximum depth of 1,332 feet, this vast body of water not only holds an impressive volume of freshwater but also influences local climate conditions and supports a diverse array of aquatic life.
Key points throughout the article highlight how Lake Superior's depth impacts:
- Thermal stratification
- Nutrient distribution
- Water quality
These impacts are often clearer when comparing average depth lake superior to the shallower Great Lakes that warm and mix more quickly. All of which are essential for maintaining healthy ecosystems. The lake’s geological history, shaped by glacial activity, further enriches its ecological dynamics, fostering habitats for various species and contributing to its relatively low pollution levels. Understanding these interconnected aspects is vital for appreciating the lake's ecological significance and the ongoing conservation efforts aimed at preserving this remarkable natural resource.
Reflecting on the importance of Lake Superior's depth reveals that this magnificent freshwater lake is not merely a body of water but a vital ecological asset that warrants protection and respect. Discussions about facts about lake superior often return to depth because it drives clarity, habitat structure, and long-term stability. Engaging in conservation initiatives and promoting awareness about the lake's unique characteristics can help ensure the well-being of its ecosystems and the communities that rely on them. Recognizing the profound impact of Lake Superior's depth on both local and global scales is essential for fostering a sustainable future for this extraordinary natural wonder.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is Lake Superior's average depth?
Lake Superior's average depth is approximately 483 feet (147 meters). This average depth of lake superior helps explain its cold-water habitats and long-lasting seasonal temperature layers.
What is the maximum depth of Lake Superior?
The maximum depth of Lake Superior reaches an impressive 1,332 feet (406 meters). This maximum depth of lake superior is why its deepest basins stay extremely cold and stable year-round.
How much water does Lake Superior hold?
Lake Superior holds around 2,900 cubic miles (12,100 km³) of water. That water volume connects to water volume of lake superior discussions about climate influence and long water-retention time.
How does Lake Superior's depth influence its ecological dynamics?
The extraordinary depth of Lake Superior influences its ecological and hydrological dynamics by enabling unique thermal layering, which impacts nutrient distribution and supports diverse aquatic ecosystems. This is a key point in many facts about lake superior, since depth shapes food webs, oxygen patterns, and ecosystem stability.
What is the significance of the cold temperatures at greater depths in Lake Superior?
The cold temperatures at greater depths create a habitat that limits bacterial growth, resulting in clearer waters and healthier fish populations. The deepest part of lake superior supports these conditions by staying cold even during summer surface warming.
How does Lake Superior compare to an ocean?
Lake Superior is often compared to an ocean due to its vast size and depth, which can lead to a misunderstanding if referred to merely as a body of water. This comparison is often reinforced by Lake Superior's shape and scale, which create an “inland sea” feel from shore.
Why is understanding Lake Superior's measurements important?
Understanding Lake Superior's measurements is vital for grasping its significant role in regional ecology and climate, highlighting its value as a natural asset and distinct environmental entity. Knowing the dimensions of lake superior supports planning for research, navigation, conservation, and shoreline development impacts.
What are some economic contributions of Lake Superior?
Lake Superior contributes economically through shipping, tourism, and recreation, underscoring its significance beyond just ecological metrics. These uses depend on stable conditions tied to lake superior depths, including routes, ports, and seasonal weather patterns.



