Overview
Lake Superior's depth is remarkable, featuring a maximum of approximately 1,333 feet and an average of 483 feet, establishing it as the largest freshwater body in North America by volume. This significant depth not only supports diverse aquatic ecosystems but also facilitates navigation for large vessels. Moreover, it plays a crucial role in regional commerce and recreation, underscoring its ecological and economic importance. Such features highlight Lake Superior's unique position, inviting further exploration and appreciation of its contributions.
Introduction
Lake Superior, the largest of the Great Lakes, commands attention with its remarkable depth measurements that not only define its physical presence but also underscore its ecological and navigational significance.
- With a maximum depth of 1,333 feet, this vast freshwater body supports a unique aquatic ecosystem while serving as a crucial artery for shipping and trade.
- However, the interplay between its profound depths and the challenges posed by invasive species and pollution raises important questions about the future of this vital resource.
- Understanding Lake Superior's depth is essential to enhancing conservation efforts and ensuring the sustainability of its rich biodiversity.
Define Lake Superior Depth: Key Measurements and Characteristics
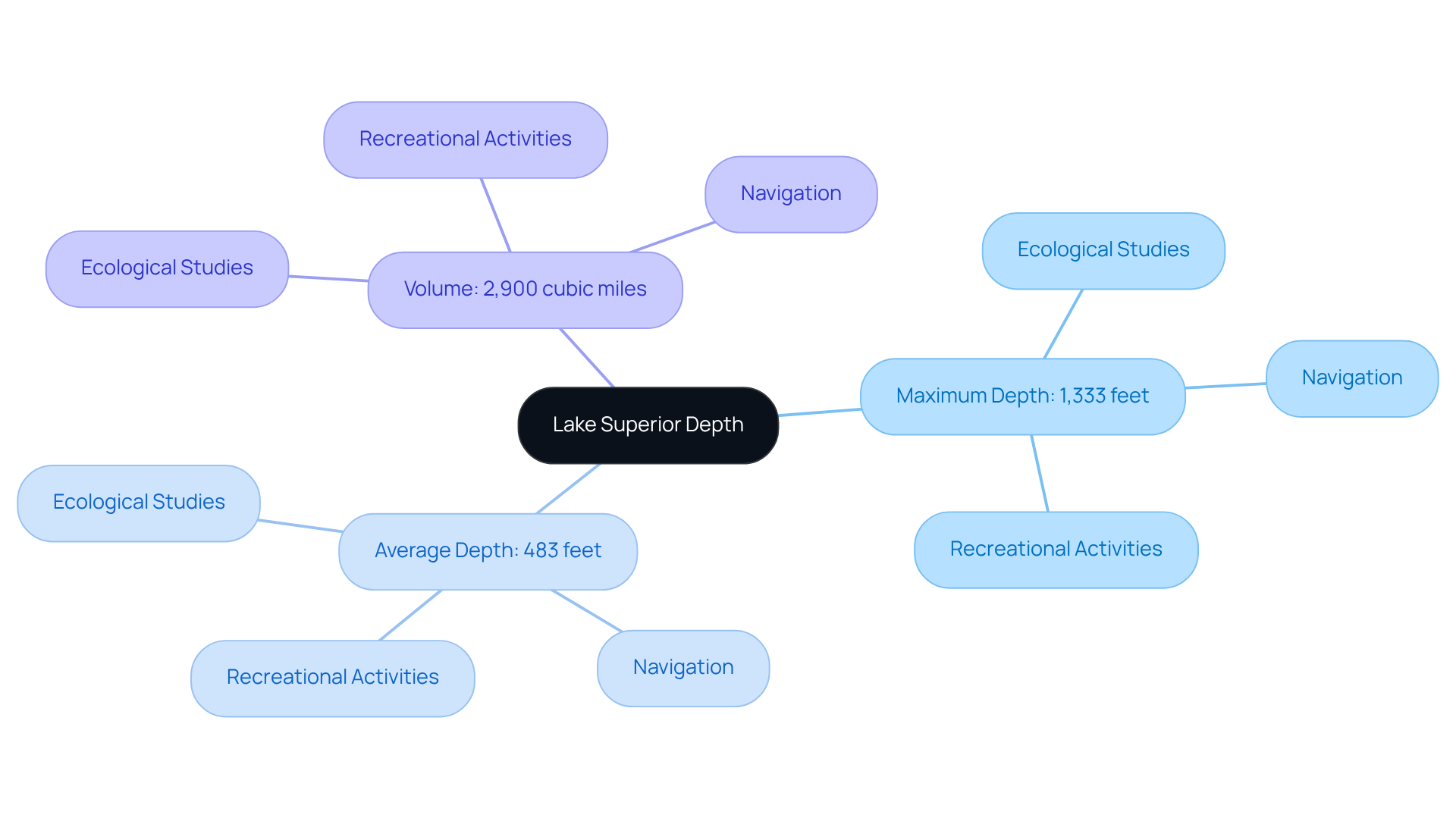
The lake superior map depth indicates that Lake Superior, recognized as the largest of the Great Lakes by surface area, has a maximum depth of approximately 1,333 feet (406 meters) and an average depth of 483 feet (147 meters). This considerable thickness contributes to its immense volume, estimated at about 2,900 cubic miles (12,100 km³), establishing it as the largest freshwater body by volume in North America, containing more water than all the other Great Lakes combined.
The lake superior map depth shows that the lake's depth varies across different regions, featuring notable underwater ridges and basins that foster a diverse aquatic environment. Understanding these measurements is crucial for various applications, including:
- Ecological studies
- Navigation
- Recreational activities
Furthermore, the lake's cold, clear waters support native fish species, such as ciscoes and lake trout, while its nutrient-poor environment limits the proliferation of invasive species, thus maintaining a delicate ecological balance. The retention duration of water in this largest freshwater lake is approximately 191 years, further emphasizing its unique characteristics.
Contextualize Lake Superior's Depth: Ecological and Navigational Importance
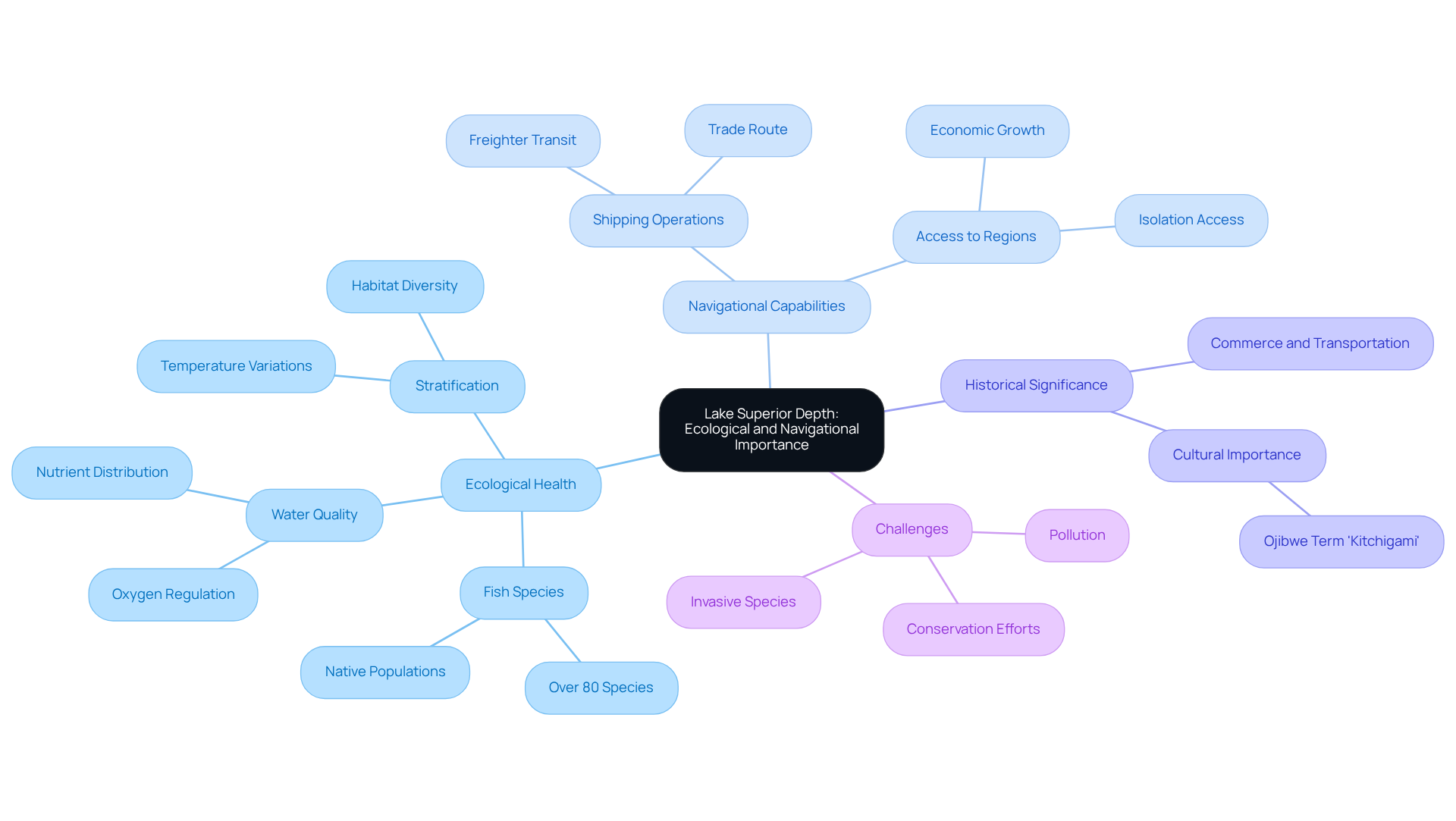
The ecological health and navigational capabilities of the lake are vital, which is reflected in the lake superior map depth. Its layering, arising from temperature variations throughout its depths, fosters diverse habitats that support over 80 species of fish, including critical native populations. This stratification is crucial for maintaining water quality by regulating oxygen levels and nutrient distribution, which are essential for a balanced ecosystem. The typical measurement of the largest freshwater body is approximately 500 feet, underscoring its ecological importance.
From a navigational perspective, the lake superior map depth reveals that Lake Superior's maximum depth of 1,332 feet allows for the secure transit of large vessels, including freighters transporting goods across the Great Lakes. The lake's expansive surface area of 31,820 square miles and its dimensions facilitate significant shipping operations, establishing it as a vital trade route. Furthermore, the lake superior map depth influences fishing habitats; deeper waters, as indicated on the lake superior map depth, provide cooler temperatures that are less conducive to bacterial growth, thereby promoting healthier fish populations.
Historically, the navigational significance of this large lake is highlighted by its role in commerce and transportation. Its profundities enable access to isolated regions and foster economic growth in nearby communities. However, challenges such as invasive species and pollution jeopardize this delicate balance, emphasizing the necessity for ongoing conservation efforts to safeguard both the ecological integrity and navigational significance of this remarkable freshwater resource. The Ojibwe term for the largest body of water in the region, 'Kitchigami,' meaning 'great water,' underscores its cultural significance, further enriching our understanding of this essential ecosystem.
Explore Historical Significance: Impact of Depth on Shipping and Recreation
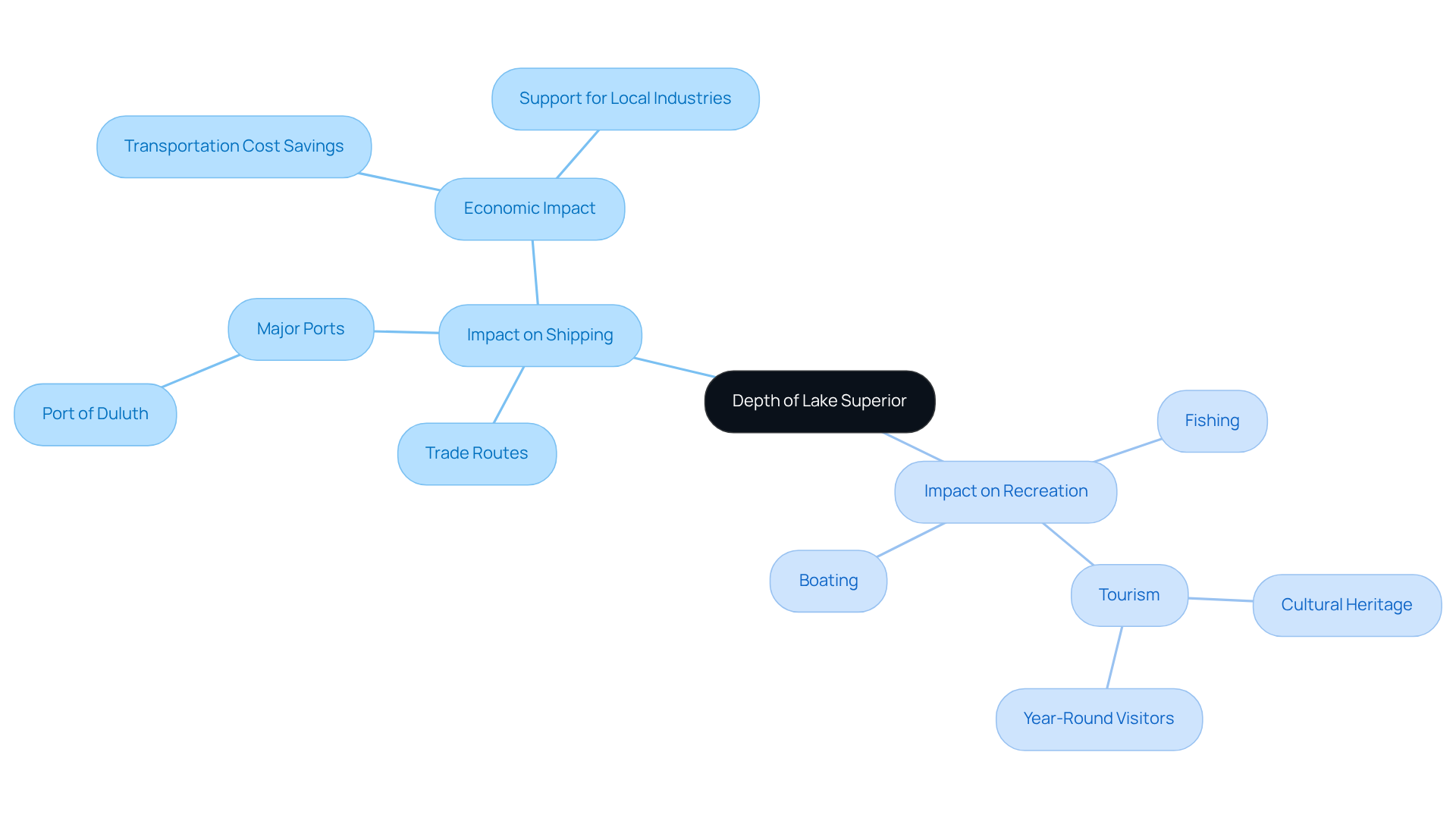
The expanse of the largest freshwater lake has historically played a crucial role in shaping shipping routes and facilitating trade. Since the early 19th century, its deep waters have enabled the transport of bulk goods, including iron ore and grain, which are vital to the regional economy. The creation of major ports, like Duluth and others, has been directly associated with the water body's navigability, facilitating efficient shipping activities that bolster local industries. In fact, the Great Lakes-St. Lawrence Seaway system saves users billions in transportation costs annually, underscoring the economic impact of these waterways.
Furthermore, Lake Superior's size not only facilitates commercial shipping but also enhances recreational opportunities. This body of water is a favored destination for fishing, boating, and tourism, contributing significantly to the local economy and cultural heritage. Specialist views emphasize that the lake's distinctive characteristics and features draw visitors throughout the year, nurturing a lively tourism industry that aids nearby communities. Consequently, the lake superior map depth is not just a geographical feature; it is an essential factor that affects commerce, economic progress, and leisure pursuits, rendering it a priceless resource for the area.
Examine Mapping Techniques: Tools and Technologies for Depth Representation
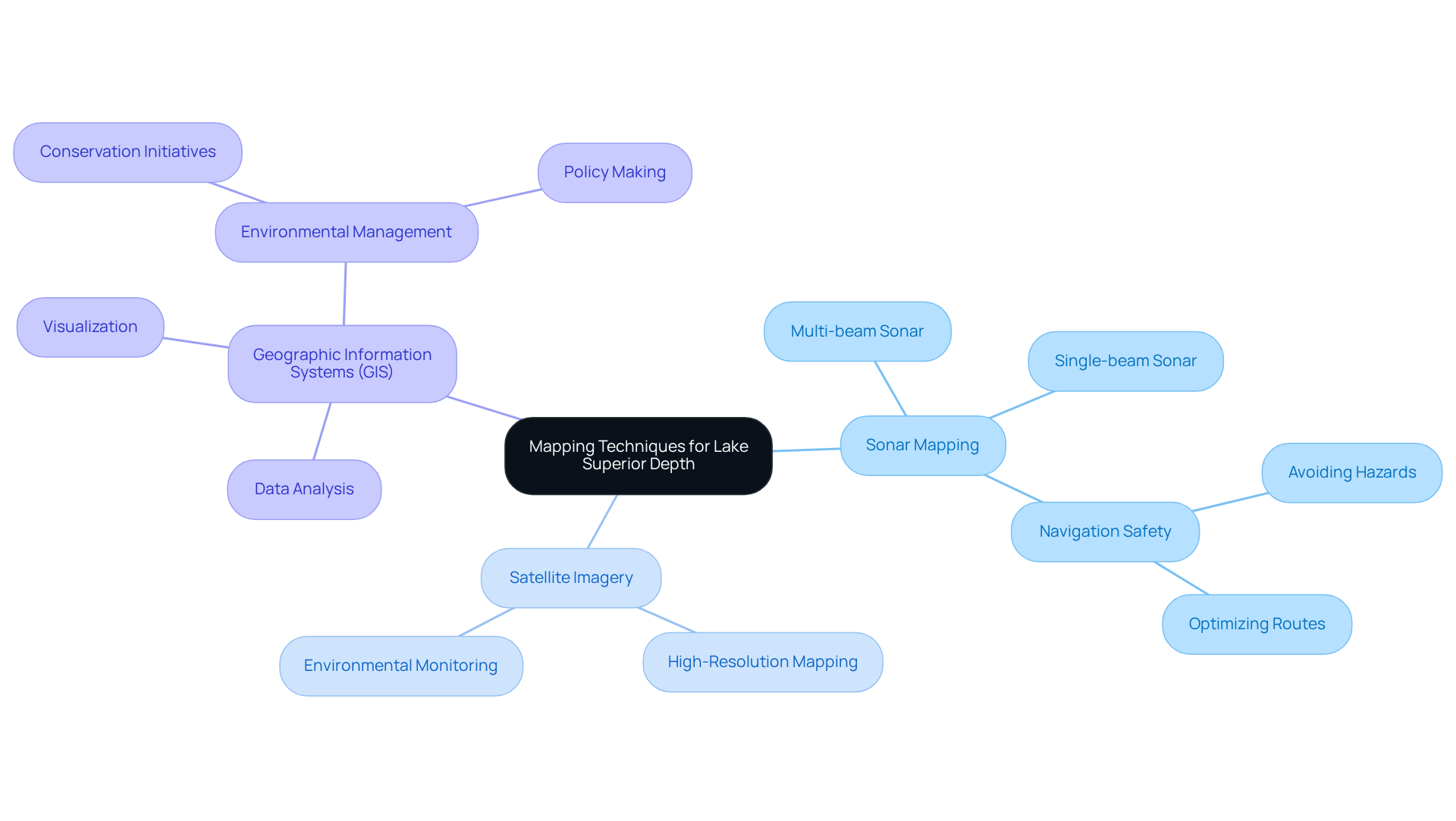
Charting the lake superior map depth employs a range of advanced methods and technologies, prominently featuring sonar mapping and satellite imagery. Multi-beam and single-beam sonar systems are instrumental in generating detailed bathymetric maps that unveil the lake superior map depth and its intricate underwater features. The lake superior map depth is essential for safe navigation, enabling vessels to avoid hazards and optimize their routes effectively.
Furthermore, Geographic Information Systems (GIS) play a pivotal role in analyzing and visualizing lake superior map depth data, empowering researchers and policymakers to make informed decisions regarding environmental management and conservation initiatives. Notably, Lake Superior contains 10 percent of the world's available surface freshwater, underscoring the critical nature of these mapping efforts.
The dataset used for these mappings was published on October 16, 2007, and has been downloaded by 210 members, indicating its significance within the community. However, users must be aware of the potential limitations of the data, as it is provided 'as is' without any warranty of accuracy or reliability, placing the burden of determining data accuracy on the user.
Conclusion
Lake Superior's depth transcends mere measurement; it is a defining characteristic that profoundly influences the lake's ecological health, navigational capabilities, and historical significance. This vast freshwater body, reaching a maximum depth of 1,333 feet and boasting an extensive volume, plays a pivotal role in sustaining diverse aquatic life and facilitating significant shipping routes that are essential for regional commerce. The intricate interplay between its depth and the surrounding environment highlights the necessity of understanding these characteristics for effective management and conservation.
Key insights reveal that the lake's depth nurtures a unique ecosystem, supporting over 80 species of fish and maintaining water quality through natural stratification. Furthermore, its navigational importance enables the safe passage of large vessels, bolstering trade and commerce in nearby communities. The historical context of Lake Superior illustrates how its depth has shaped economic activities and recreational opportunities, rendering it a treasured resource for both local residents and visitors alike.
Ultimately, acknowledging the multifaceted importance of Lake Superior's depth necessitates a commitment to safeguarding this invaluable freshwater resource. Ongoing conservation efforts are crucial to protecting its ecological integrity and navigational significance, ensuring that future generations can continue to benefit from the rich heritage and resources that Lake Superior offers. Engaging with and advocating for the preservation of such a remarkable natural asset is vital for sustaining the delicate balance between human activity and ecological health.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is the maximum depth of Lake Superior?
The maximum depth of Lake Superior is approximately 1,333 feet (406 meters).
What is the average depth of Lake Superior?
The average depth of Lake Superior is 483 feet (147 meters).
How does the depth of Lake Superior contribute to its volume?
The considerable depth of Lake Superior contributes to its immense volume, which is estimated at about 2,900 cubic miles (12,100 km³), making it the largest freshwater body by volume in North America.
What ecological studies are influenced by Lake Superior's depth?
The depth of Lake Superior is crucial for ecological studies, navigation, and recreational activities.
What types of fish are supported by Lake Superior's waters?
Lake Superior's cold, clear waters support native fish species such as ciscoes and lake trout.
How does the nutrient environment of Lake Superior affect invasive species?
The nutrient-poor environment of Lake Superior limits the proliferation of invasive species, helping to maintain a delicate ecological balance.
What is the retention duration of water in Lake Superior?
The retention duration of water in Lake Superior is approximately 191 years.


