Overview
Lake Superior, with an average depth of 483 feet and a remarkable maximum depth of 1,332 feet, stands out as the largest and deepest of the Great Lakes. This significant depth not only distinguishes it but also plays a critical role in shaping its ecological health and supporting local economies. The article underscores how this extraordinary depth fosters a diverse array of aquatic species and recreational opportunities. Furthermore, it highlights Lake Superior's vital importance as a freshwater resource that sustains local communities and bolsters economic activities such as tourism and fishing.
Introduction
Lake Superior, the crown jewel of the Great Lakes, commands attention not only for its impressive size but also for its remarkable depth, reaching a staggering maximum of 1,332 feet. This immense underwater landscape is pivotal in shaping the lake's ecology, influencing critical factors such as water temperature and the diversity of species that thrive within its depths. As the largest freshwater resource in North America, Lake Superior is vital for its rich ecosystems and the local economies that rely on its recreational and commercial opportunities.
However, this natural wonder faces significant challenges from rising nitrate levels and invasive species, prompting urgent research to safeguard its future. Understanding the intricate relationship between the lake's depth and its ecological health is essential for preserving this critical resource for generations to come.
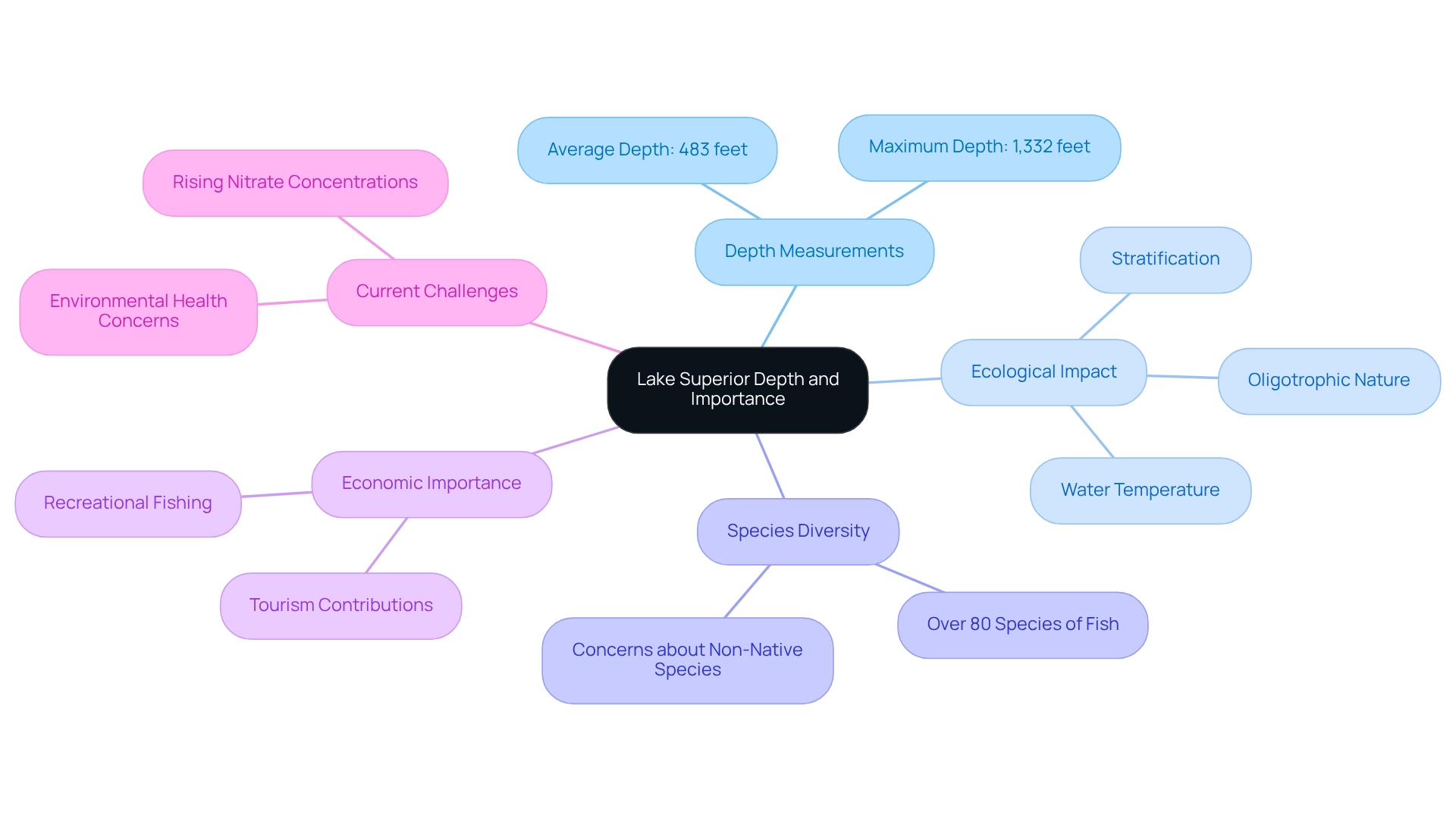
Understanding Lake Superior's Depth and Its Importance
The largest and deepest of the Great Lakes, the depth of Lake Superior boasts an impressive average measurement of 483 feet and a maximum measurement of 1,332 feet. This remarkable extent is essential for the lake's ecology, significantly affecting water temperature, stratification, and the variety of species that reside in its waters. As a crucial freshwater resource, the largest of the Great Lakes holds around 10% of the planet's surface freshwater, underscoring its significance not only to regional ecosystems but also to local communities and sectors such as tourism and fishing.
The depth of Lake Huron plays a pivotal role in maintaining its oligotrophic nature, which supports over 80 species of fish. However, recent ecological studies have raised concerns about rising nitrate concentrations and the introduction of non-native species, which threaten this delicate balance. Current studies aim to address these challenges and ensure the sustainability of the fish populations in this vital body of water.
Dan Bevilacqua, Executive Director of Ontario’s Superior Country, emphasizes the need to promote the region, stating that he is constantly seeking ways to highlight its natural beauty and ecological significance. He observes that the depth of Lake Superior not only influences its ecological health but also affects local economies that rely on recreational fishing and tourism. For instance, the body of water's status as the lowest point of land in North America and the largest recorded waves of 28.8 feet illustrate its dynamic nature. Understanding and managing this critical resource is essential for stakeholders.
Comparative Depths of the Great Lakes
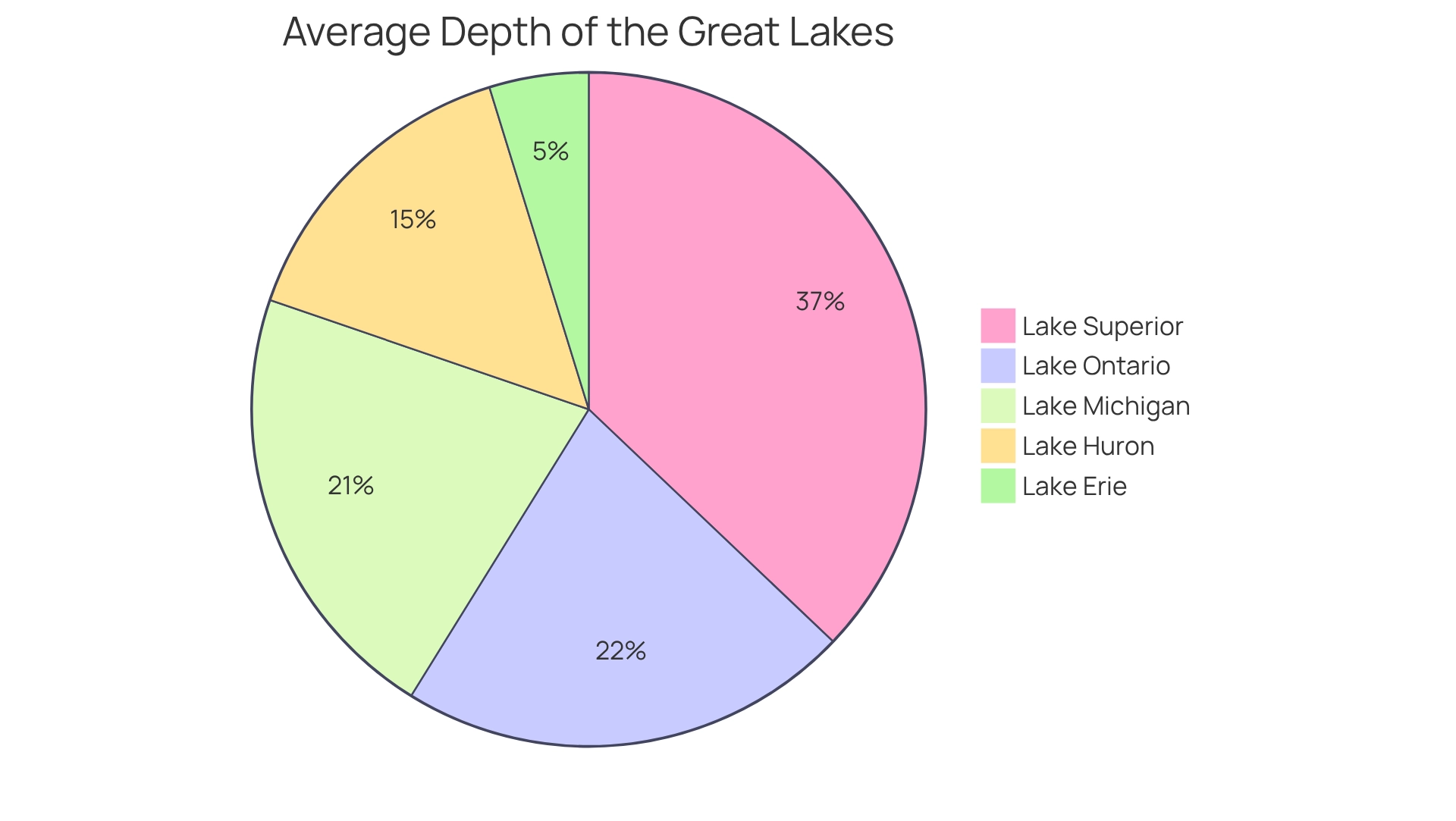
In the realm of the Great Lakes, the depth of Lake Superior makes it stand out as the largest, deepest, and most voluminous body of water. The following measurements underscore this remarkable characteristic:
- Lake Superior: Average measurement of 483 feet; Maximum measurement of 1,332 feet.
- Lake Michigan: Average measurement of 279 feet; Maximum measurement of 925 feet.
- Lake Huron: Average measurement of 195 feet; Maximum measurement of 750 feet.
- Lake Erie: Average measurement of 62 feet; Maximum measurement of 210 feet.
- Lake Ontario: Average measurement of 283 feet; Maximum measurement of 802 feet.
This comparison highlights Lake Superior's dominance, as it contains more water than the other four lakes combined, solidifying its status as the largest by volume. Such richness fosters distinctive ecological conditions that support diverse habitats. The significance of these waters is further illustrated by the Great Lakes' substantial contribution to trade; their extensive shipping routes, bolstered by canals and tributaries, connect to the Mississippi River, enhancing economic activities across North America. Notably, as observed by the National Park Service, the depth of Lake Superior, referred to as Kitchigami or 'great lake' in Ojibwe, embodies not only natural beauty but also essential resources, including drinking water for 40 million people. This combination of richness and ecological importance reinforces the status of this vast body of water as a crucial resource among the Great Lakes.
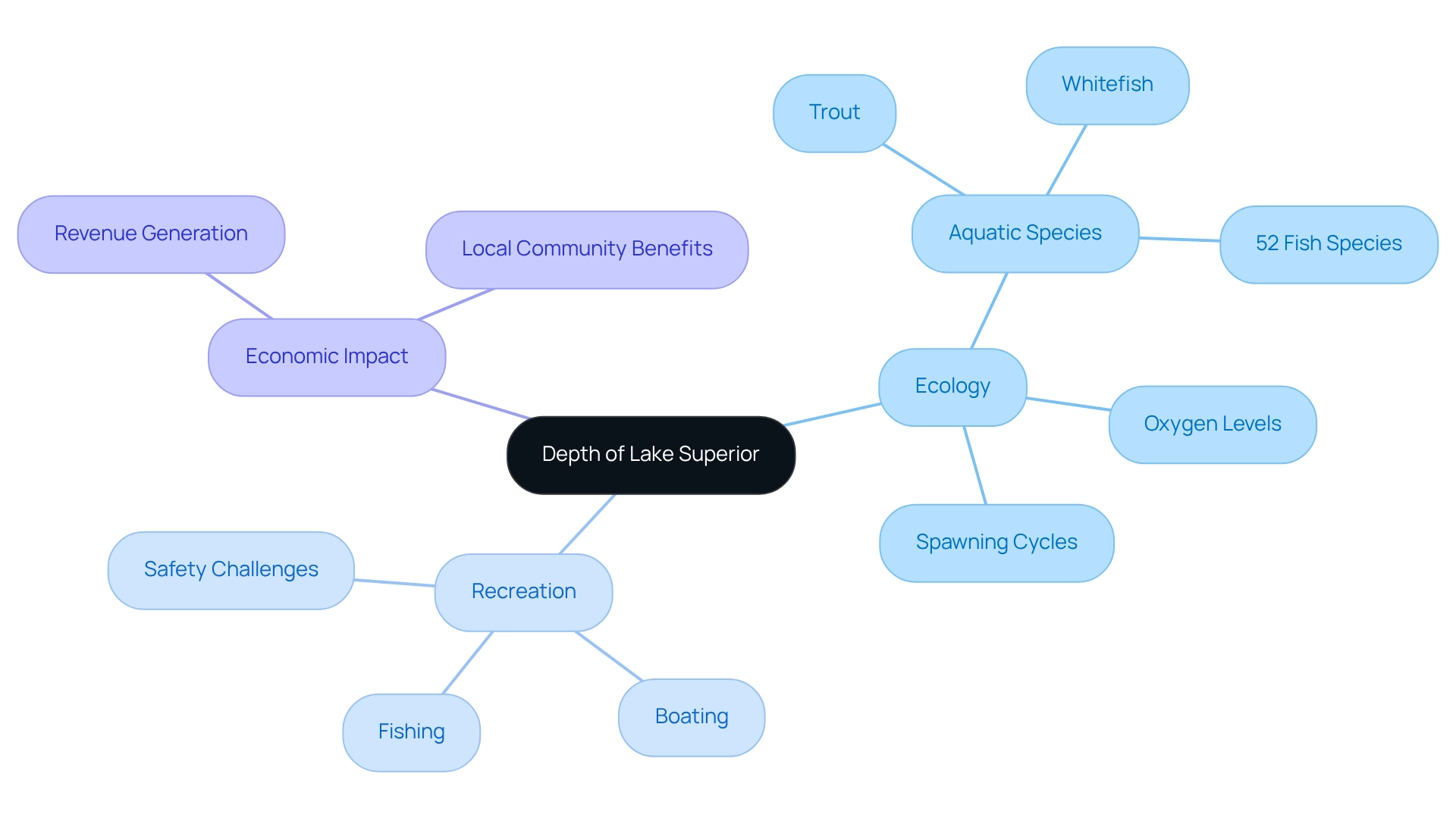
Impact of Depth on Ecology and Recreation
The vastness of Lake Superior, along with the depth of Lake Superior, significantly influences its ecology and recreational activities. The cold, deep waters of the depth Lake Superior create a unique environment that supports a variety of aquatic species, including native fish such as trout and whitefish. The stratification of water due to the depth of Lake Superior affects oxygen levels and temperature, which in turn impacts fish populations and their spawning cycles.
From a recreational standpoint, the depth of Lake Superior facilitates a range of activities, including deep-water fishing, boating, and kayaking, attracting both tourists and locals alike. The lake's immense size allows for the accommodation of larger vessels, establishing it as a hub for shipping and transportation. However, this vastness also presents challenges, particularly the potential for dangerous conditions during storms, necessitating careful management to ensure the safety of all users.
In 2025, the economic impact of recreational fishing and tourism around Lake Superior continues to be substantial, with these activities generating significant revenue for local communities. The interaction between the depth of Lake Superior and its aquatic life not only enriches the recreational experience but also bolsters the local economy, making it an essential resource for the surrounding areas.
Conclusion
The exploration of Lake Superior’s remarkable depth unveils its critical role in maintaining ecological balance and supporting diverse aquatic life. With a maximum depth of 1,332 feet, the lake serves not only as a vital freshwater resource but also sustains over 80 species of fish, underscoring its importance to regional ecosystems and local economies. The ongoing challenges posed by rising nitrate levels and invasive species highlight the urgency of research and conservation efforts needed to protect this unique aquatic environment.
In comparison, Lake Superior stands out among the Great Lakes, holding more water than all the other lakes combined. This dominance in depth and volume enhances its ecological significance and economic value, as it supports extensive shipping routes and recreational activities. The lake’s cold, deep waters create ideal habitats for native fish species, while also providing opportunities for deep-water fishing and tourism, essential for local communities.
Ultimately, understanding the interplay between Lake Superior’s depth and its ecological health is paramount for ensuring sustainability. As pressures from environmental changes increase, safeguarding this natural treasure is essential—not only for preserving its rich biodiversity but also for supporting the livelihoods of those who depend on its resources. The future of Lake Superior hinges on collective efforts to protect and manage this vital freshwater ecosystem for generations to come.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is the average and maximum depth of Lake Superior?
Lake Superior has an average depth of 483 feet and a maximum depth of 1,332 feet.
Why is the depth of Lake Superior important for its ecology?
The depth of Lake Superior significantly affects water temperature, stratification, and the variety of species that reside in its waters.
What percentage of the planet's surface freshwater does Lake Superior hold?
Lake Superior holds around 10% of the planet's surface freshwater.
What ecological challenges is Lake Huron currently facing?
Lake Huron is facing rising nitrate concentrations and the introduction of non-native species, which threaten its oligotrophic nature and the sustainability of its fish populations.
How many species of fish does Lake Huron support?
Lake Huron supports over 80 species of fish.
What role does Dan Bevilacqua play regarding Lake Superior?
Dan Bevilacqua is the Executive Director of Ontario’s Superior Country, and he emphasizes the need to promote the region's natural beauty and ecological significance.
How does the depth of Lake Superior affect local economies?
The depth of Lake Superior influences its ecological health, which in turn affects local economies that rely on recreational fishing and tourism.
What notable features are associated with Lake Superior?
Lake Superior is noted for being the lowest point of land in North America and has recorded waves as large as 28.8 feet.


