Overview
A world map serves as a powerful graphical representation of the Earth's surface, illustrating both political and physical features that enhance our understanding of global geography and spatial relationships. A well-made map of the world helps readers compare places quickly, even when they have never traveled there before. Its significance extends beyond mere representation; it plays a crucial role in navigation, education, and cultural representation. Many learners start with different types of world maps to see how each style changes what stands out. Furthermore, the design elements—such as projections and symbols—are not only functional but also enhance the aesthetic appeal of the map, making it a vital tool for both learning and exploration.
Introduction
A world map transcends mere visual representation of the Earth's surface; it serves as a gateway to understanding the intricate relationships that define our planet. For students and travelers alike, a world geography map often becomes the easiest way to connect names on a page to real places in the world. These maps play crucial roles in education, navigation, and business strategy, offering insights into geographical features, political boundaries, and cultural contexts. In modern gifting, presents for map lovers have grown in popularity because they blend decor with personal meaning. Yet, the art of map-making is fraught with challenges, particularly the distortions that occur when translating a spherical world onto a flat surface.
- How do these distortions influence our perception of geography?
- What innovations in design have emerged to enhance our understanding of the world?
- How do different kinds of world maps change what we notice first: borders, terrain, or oceans?
This exploration is not just academic; it invites inquiries into the craftsmanship and personalization of maps, crafted with care to capture unique stories and perspectives.
Define World Map: A Comprehensive Overview
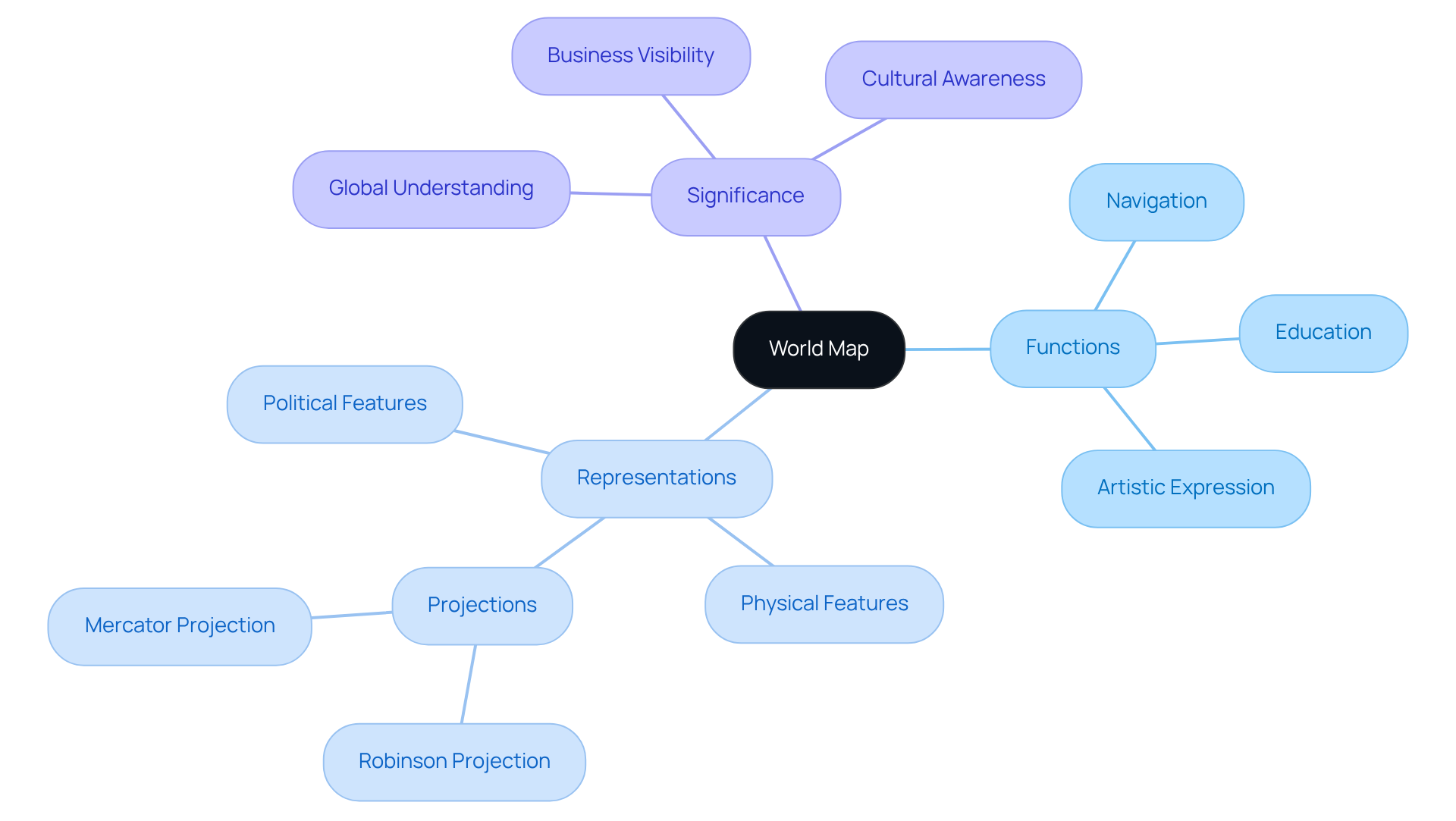
A world map serves as a powerful graphical representation of the Earth's surface, illustrating both political and physical features, including continents, countries, oceans, and notable geographical landmarks. A world map that shows countries is especially useful when readers want to understand borders, labels, and how nations relate to each other. These maps vary in scale and detail, fulfilling diverse functions such as navigation, education, and artistic expression. A detailed map of the oceans can also support learning by showing how water connects continents and shapes global movement. They are essential for comprehending global geography and spatial relationships, allowing individuals to envision the planet in a simplified manner.
The design of a world map often employs different representations to accurately portray the spherical Earth on a two-dimensional world map surface. On some designs, a bathymetry map adds extra realism by showing underwater contours instead of a flat blue ocean fill. This intricate process can introduce distortions in size, shape, and distance, which are critical considerations in map-making. For instance, the Robinson projection is favored for its balanced depiction of landmasses, making it a popular choice in educational contexts and corporate gifting.
Statistics reveal that over 200 million businesses and locations are listed on Google Maps, underscoring the significance of accurate geographical representation in enhancing visibility and accessibility for businesses. In that same spirit, Google Maps gifts can turn meaningful addresses and routes into a display piece people actually keep. Moreover, expert insights emphasize that the world map is not merely a navigation instrument; it also acts as an artistic representation that ignites creativity and inspires discovery. In educational settings, they play an essential role in teaching geography, aiding students in grasping complex spatial concepts and fostering a deeper awareness of their surroundings. For that reason, gifts for geography lovers often include maps that feel both educational and personal.
Trace the Evolution: Historical Context of World Maps
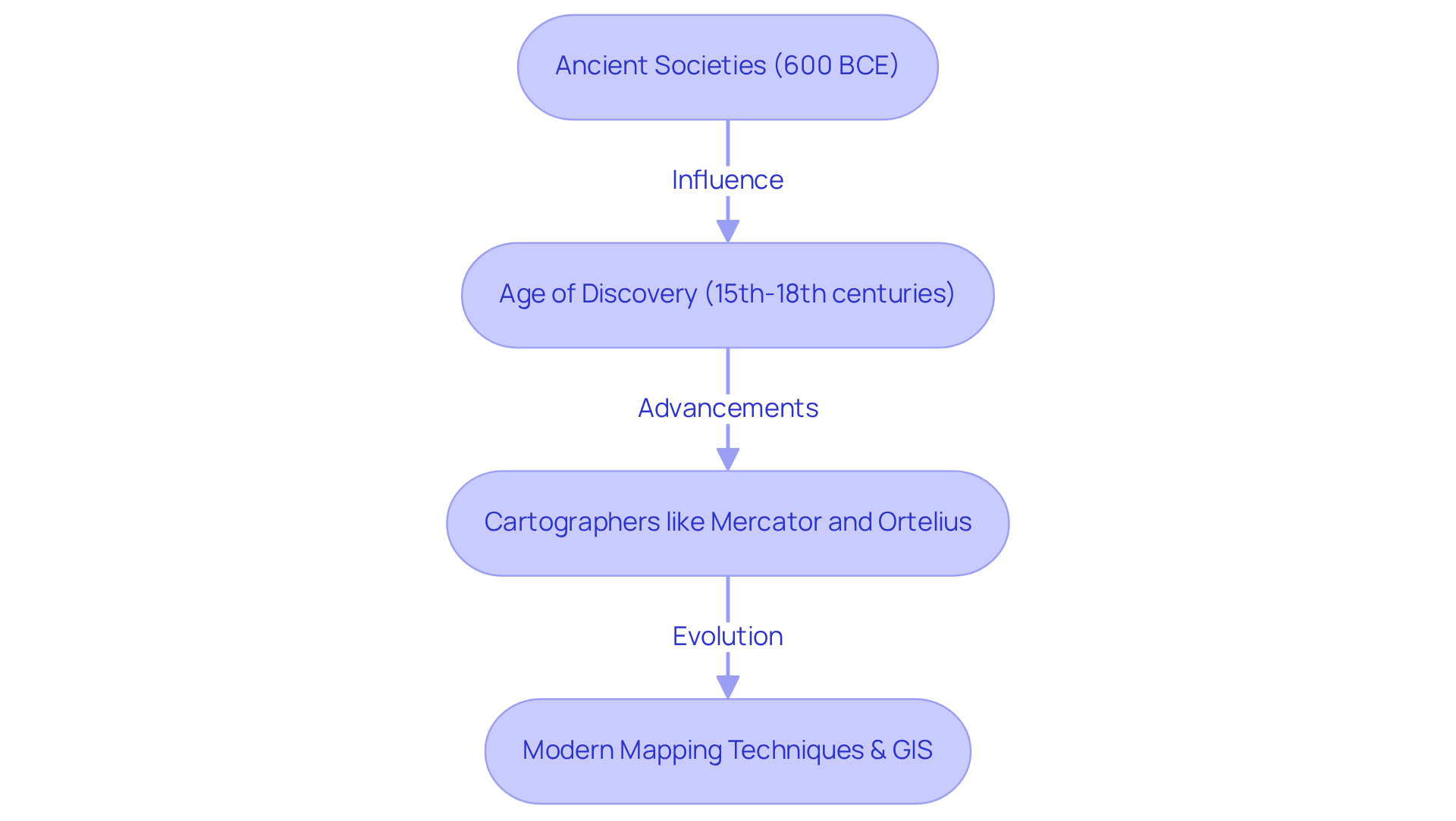
The development of the world map is a remarkable journey that traces its origins to ancient societies, with the oldest recognized instances emerging from Babylon around 600 BCE. When historians describe early cartography, they are still referring to a world map, even if the version reflects limited knowledge of the time. These early maps, though simplistic, laid the foundation for our understanding of geography, often depicting the world as flat and focusing on local landscapes.
As exploration flourished during the Age of Discovery from the 15th to the 18th centuries, cartographers began to create more precise representations of the world map, incorporating new findings and advancements in navigation. During this period, world mapping became tightly linked to trade routes, sea travel, and the need for more accurate coastlines. Notable figures such as Gerardus Mercator and Abraham Ortelius played pivotal roles in refining modern map-making techniques.
The introduction of various map representations, such as the innovative Mercator technique, enhanced the depiction of the Earth's surface, despite the inherent distortions these methods introduced. As interest in seas and coastlines expanded, bathymetric maps also became valuable for documenting underwater features important to navigation. Today, the world map continues to evolve alongside technological advancements, embracing digital plotting and Geographic Information Systems (GIS). Collectors now seek unique world maps that reflect personal journeys, not just general reference.
This ongoing development underscores the craftsmanship and personalization that define modern mapping, inviting inquiries and engagement from those interested in exploring the world through these sophisticated tools.
Examine Design Elements: Key Characteristics of World Maps
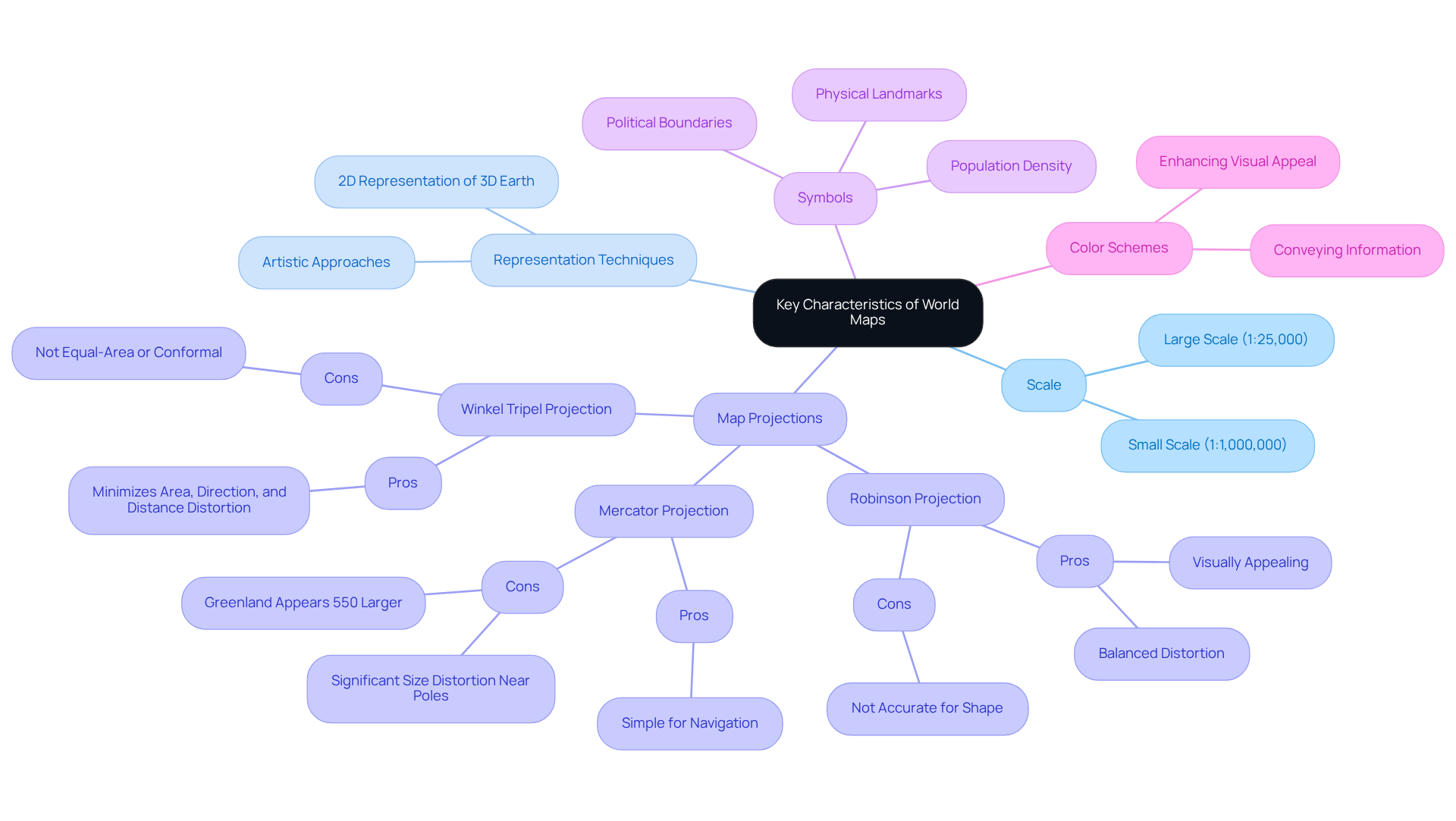
World maps possess distinctive features that are essential for understanding their significance, including scale, representation, symbols, and color schemes. The scale of a world map determines the level of detail and the area depicted, while the mapping technique influences how the three-dimensional Earth is represented on the two-dimensional surface of the world map. The scale of the world map determines the level of detail and the area depicted, while the mapping technique influences how the three-dimensional Earth is represented on the two-dimensional surface of the world map. Notable representations on the world map include the Robinson, introduced in 1963, Mercator, and Winkel Tripel, each presenting unique benefits and drawbacks related to distortion. For example, the Mercator world map significantly distorts country sizes, particularly near the poles, making Greenland appear 550% larger than its actual size—an important consideration for grasping geographical relationships. Conversely, the Robinson world map provides a more visually appealing representation by balancing area and shape distortions, while the Winkel Tripel design minimizes distortions in area, direction, and distance, resulting in a more accurate depiction of the globe. Many educators rely on different kinds of world maps like these to teach students why “accuracy” depends on what the map is designed to show. Arthur Robinson, the mastermind behind the Robinson design, noted that he approached map-making with an artistic vision, focusing on the most aesthetically pleasing shapes and sizes before developing the mathematical formula to achieve that effect.
Symbols on a world map serve to represent various features, including political boundaries, physical landmarks, and population density, while color schemes effectively convey information about diverse regions, climates, or cultural aspects. A labeled map of the world often uses these symbols and color choices to make boundaries and place names easier to interpret at a glance. The U.S. Geological Survey utilizes over 18 different world map projections for various applications, underscoring the necessity of selecting appropriate projections tailored to specific needs. Effective world map design strikes a balance between aesthetic appeal and clarity, ensuring that the world map fulfills its intended purpose while remaining visually engaging. In modern decor and collecting, unique world maps often lean into this balance, combining strong design with readable geography. Elements such as legends, titles, and scale bars are critical for providing context and enhancing usability on a world map. Current trends in cartographic design highlight the significance of these features, ensuring that the world map not only serves its intended function but also captivates viewers visually.
Explore Significance: The Role of World Maps Today
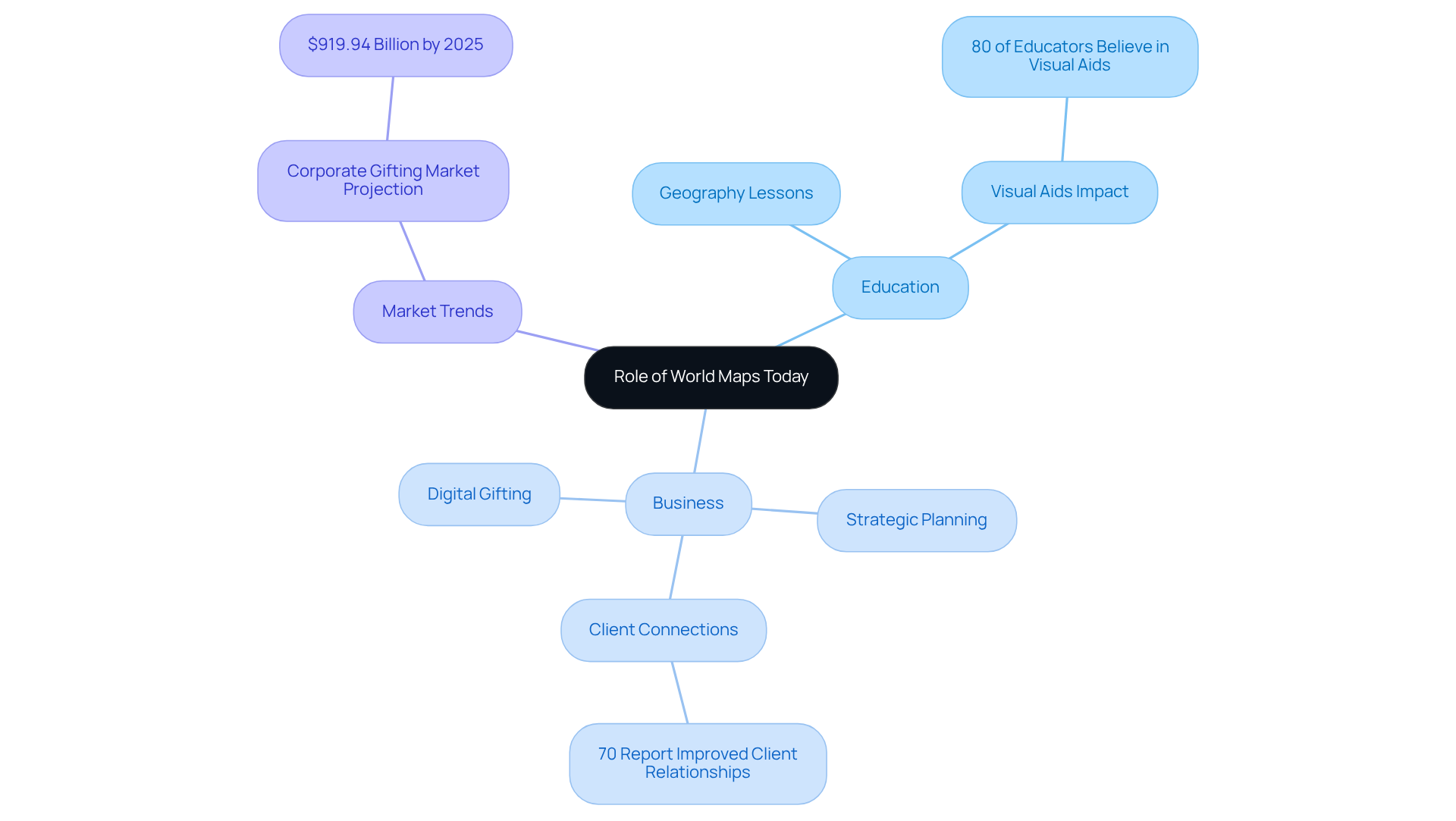
Global representations serve as essential instruments in education, navigation, and cultural portrayal. In educational environments, they facilitate geography lessons, enabling students to effectively grasp spatial relationships and global issues. A study reveals that 80% of educators believe visual aids, such as charts, significantly enhance learning outcomes. For many classrooms, a geographical world map is the most direct way to introduce regions, continents, and global connections.
In the business sector, geographic representations are utilized for strategic planning, market analysis, and as distinctive gifts that resonate with clients and employees. This is also why gifts for map lovers and premium map decor have become popular in corporate and personal settings. Customized charts from Pangea Maps, showcasing important milestones or collective experiences, can strengthen business relationships, with 70% of companies reporting improved client connections through thoughtful gifting. Each map is handcrafted over bathymetry, illustrating the water's topography, and is custom-designed to narrate a unique story, taking approximately an hour to create. For ocean-themed storytelling, a water depth map adds detail that feels personal, especially when a coastline or travel memory is central to the design.
The corporate gifting market is projected to reach $919.94 billion by 2025, underscoring the importance of personalized gifts in today's business landscape. Many brands now choose custom map gifts because they are display-worthy and naturally spark conversation in offices and homes. The rise of digital formats has further increased the utility of global charts, enabling interactive exploration and data visualization. This capability assists organizations in making informed decisions based on geographical data, including climate change impacts, population trends, and resource distribution.
Additionally, 60% of businesses anticipate that digital gifting platforms will replace traditional ordering methods, highlighting the shift towards digital solutions in corporate gifting. Consequently, world maps are invaluable resources that cultivate a deeper understanding and appreciation of our interconnected world. For anyone shopping for gifts for geography lovers, this mix of learning, design, and storytelling is exactly what makes maps timeless.
Conclusion
A world map is not merely a simple representation of geography; it embodies a complex interplay of design, history, and functionality that significantly enhances our understanding of the Earth. By illustrating both political and physical features, these maps serve as vital tools for navigation, education, and cultural expression, allowing individuals to visualize and engage with the world around them. For daily reference, many people still rely on maps of the world because they provide context that a list of place names cannot.
The evolution of world maps has been traced from their ancient origins to modern technological advancements. Key insights highlight the importance of various mapping techniques, such as the Robinson and Mercator projections, which balance aesthetic appeal with accuracy. Exploring different types of world maps helps readers understand why one design might be better for learning, while another works better for navigation or decor. Furthermore, the role of world maps in education and business underscores their significance in fostering spatial awareness and facilitating strategic decision-making.
In an increasingly interconnected world, the value of world maps extends beyond mere navigation. They are essential instruments that promote understanding and appreciation of global dynamics. Engaging with world maps encourages exploration, creativity, and informed decision-making, making them invaluable resources in both personal and professional contexts. For collectors and gift-givers, this is why map gift ideas remain popular, because a good map can be both meaningful and useful at the same time. Embracing this knowledge can inspire individuals and organizations alike to deepen their geographical literacy and enhance their global perspective.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is a world map?
A world map is a graphical representation of the Earth's surface that illustrates political and physical features, including continents, countries, oceans, and notable geographical landmarks. A clear map of the earth helps viewers understand where places sit in relation to each other, not just what they are called.
What are the main functions of a world map?
World maps serve various functions such as navigation, education, and artistic expression, helping individuals comprehend global geography and spatial relationships. Many educators use a geography map of the world to teach regions, borders, and the way continents connect through land and sea.
How does a world map represent the spherical Earth?
The design of a world map often employs different representations to portray the spherical Earth on a two-dimensional surface, which can introduce distortions in size, shape, and distance. This is why exploring different kinds of world maps is helpful, because each projection makes certain features look more accurate than others.
What is the Robinson projection?
The Robinson projection is a type of map projection favored for its balanced depiction of landmasses, making it popular in educational contexts and for corporate gifting. It’s often chosen when people want the worldwide map to look visually balanced while still staying readable.
How significant is the use of maps in business?
Over 200 million businesses and locations are listed on Google Maps, highlighting the importance of accurate geographical representation for enhancing visibility and accessibility for businesses. This is also why Google Maps gifts have become popular, because they turn real business locations and routes into memorable keepsakes.
Besides navigation, what other roles does a world map play?
A world map acts as an artistic representation that inspires creativity and discovery, and it plays a crucial role in education by helping students understand complex spatial concepts and fostering awareness of their surroundings. That storytelling value is also why map presents gifts and other gifts for map enthusiasts remain timeless for collectors and travelers.



