Overview
The depth of Lake Superior commands attention, with an average depth of approximately 500 feet and a maximum depth of 1,332 feet. This remarkable depth not only contributes to its vast water volume but also shapes unique ecosystem dynamics. Such significant depth affects temperature stratification, supports a diverse array of aquatic life, and plays an essential role in the hydrology and conservation efforts of the surrounding region. Understanding these dynamics is crucial for appreciating the ecological value and conservation needs of this magnificent lake.
Introduction
Lake Superior, a colossal freshwater body revered as 'Kitchigami' in Ojibwe, captivates with its remarkable depths that shape its ecosystem and geological history. With an average depth of around 500 feet and a maximum plunge of 1,332 feet, this lake not only influences local biodiversity but also plays a crucial role in temperature stratification and nutrient distribution.
However, what challenges arise from such profound depths? How do they impact the surrounding environment and communities reliant on this vital natural resource? Exploring these questions unveils the intricate connections between Lake Superior's depth, its ecological significance, and the ongoing conservation efforts aimed at preserving this landmark.
The depth of Lake Superior is not merely a statistic; it is a testament to the lake's role as a cornerstone of ecological health and community resilience.
Define Lake Superior's Depth
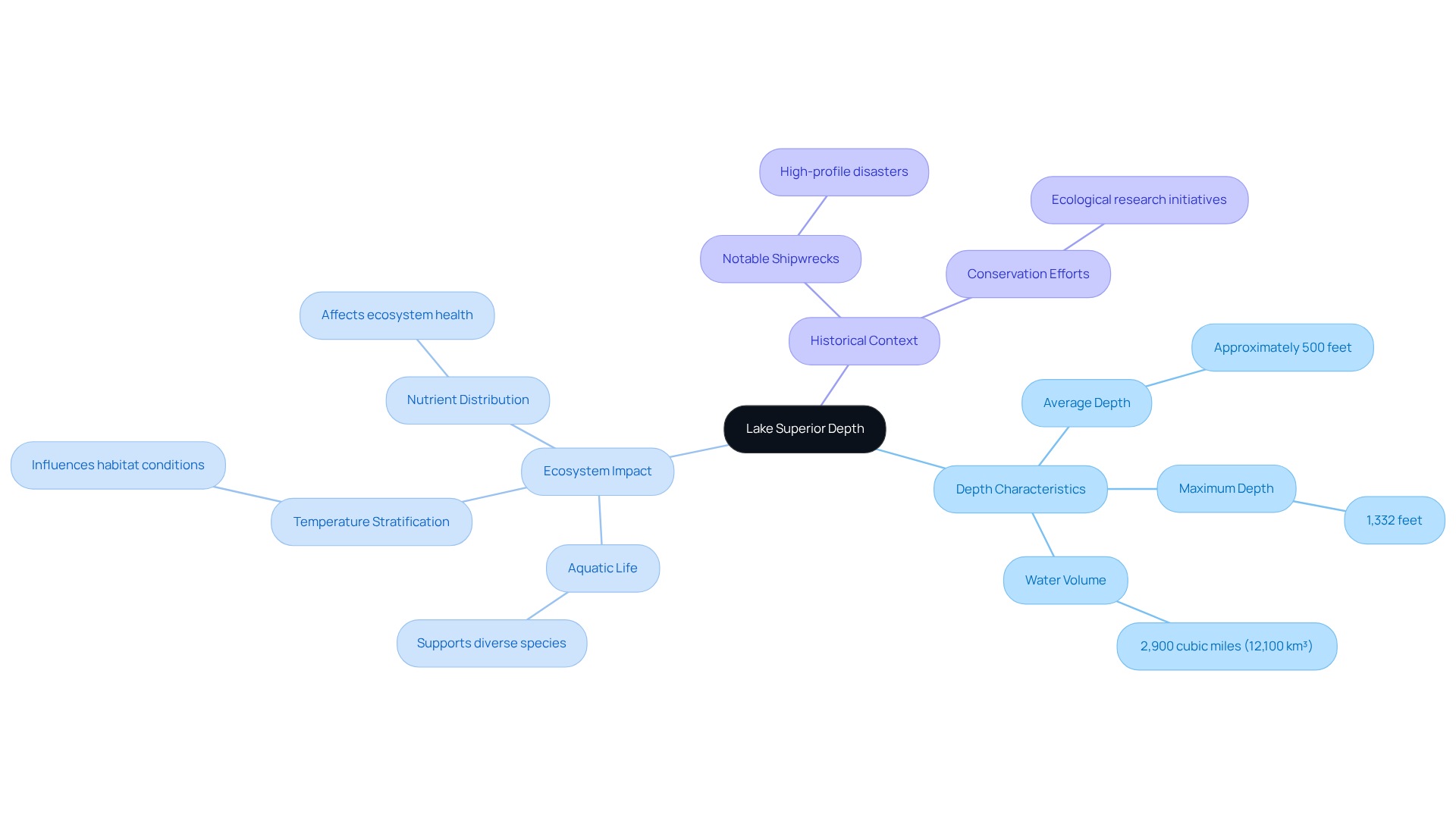
Lake Superior, the largest of the Great Lakes by surface area, is known in Ojibwe as 'Kitchigami,' which translates to 'great body of water.' The depth of Lake Superior map illustrates an impressive average depth of approximately 500 feet (152 meters) and a maximum depth of 1,332 feet (406 meters). This remarkable depth contributes significantly to its vast water volume, estimated at 2,900 cubic miles (12,100 km³), and plays a crucial role in the lake's temperature stratification and overall ecosystem health.
The depth of Lake Superior map profoundly influences the hydrology of this largest freshwater body, affecting everything from aquatic life to nutrient distribution. For instance, the cold, deep waters create a unique habitat that supports diverse species, including fish that thrive in cooler temperatures. Additionally, the regions surrounding the lake, such as Isle Royale National Park, are home to fauna like wolves and moose, underscoring the biodiversity sustained by this ecosystem.
The historical context of Lake Superior is also marked by notable shipwreck disasters, emphasizing its formidable nature. This intricate connection between the depth of Lake Superior map and ecosystem dynamics establishes the area as a vital region for ecological research and conservation initiatives.
Contextualize Within the Great Lakes
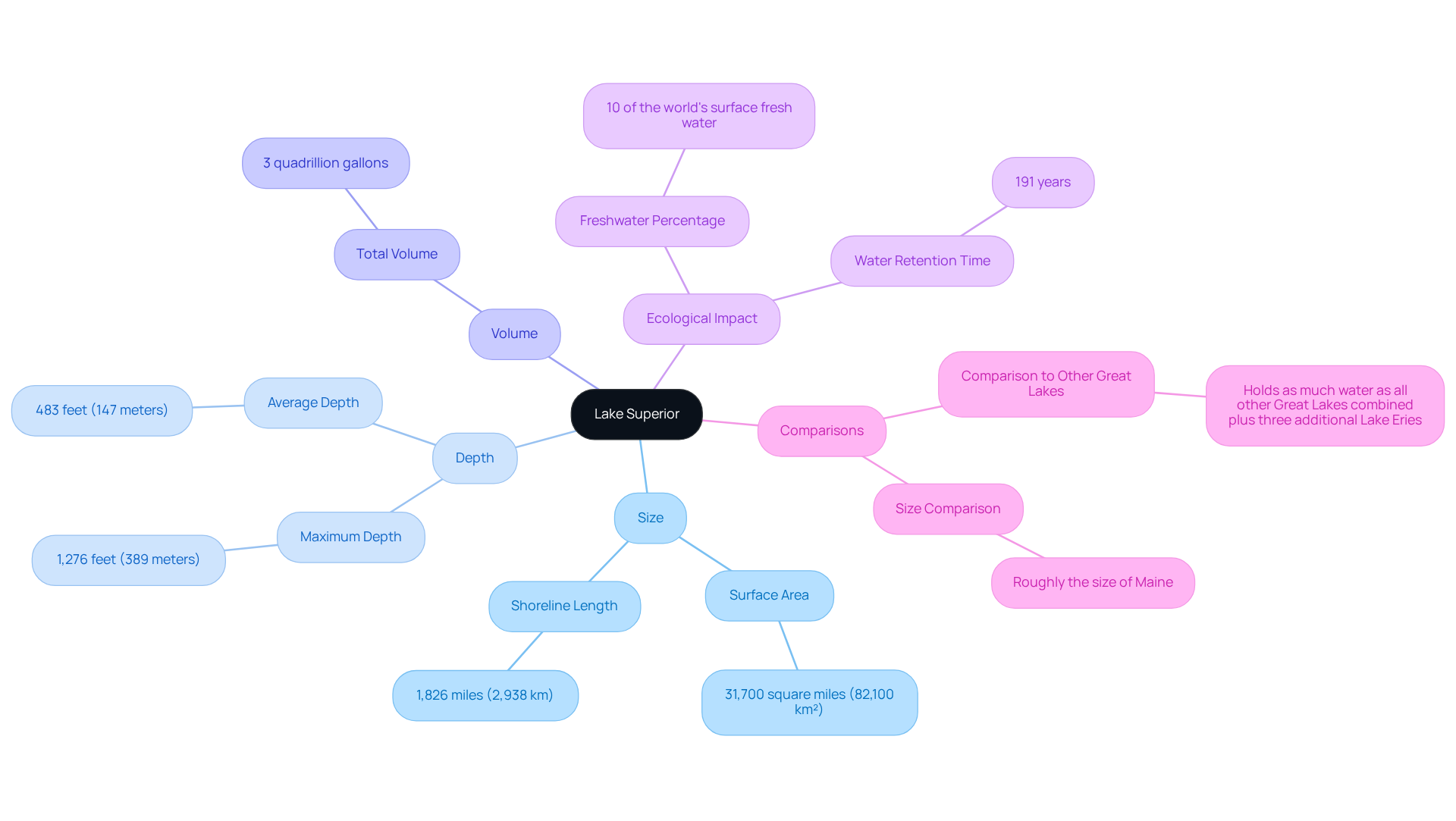
Lake Superior, the largest of the Great Lakes, is not only the deepest but also the most extensive by surface area, spanning approximately 31,700 square miles (82,100 km²). In comparison, Michigan's largest body of water, which ranks second in surface area, has a maximum depth of 923 feet (281 meters).
The extraordinary profundity of Lake Superior, as indicated on the depth of Lake Superior map, reaches a maximum of 1,276 feet (389 meters), with an average depth of 483 feet (147 meters). This remarkable depth contributes to its distinctive thermal dynamics, which differ from those of other bodies of water, thereby impacting local weather patterns and the variety of fish species that thrive in its waters.
Furthermore, the depth of Lake Superior map plays a crucial role in the lake's capacity to store and regulate water, making it an essential resource for surrounding communities and ecosystems. Lake Superior's water retention time is approximately 191 years, further illustrating its unique characteristics compared to other Great Lakes.
The vast volume of this large body of water, estimated at 3 quadrillion gallons, underscores its significance, as it contains enough water to cover North and South America under a foot of water. As Steve Colman, a retired authority from the University of Minnesota Duluth's Large Lakes Observatory, notes, "It's the world's largest freshwater body by surface area - 31,700 square miles (82,100 square kilometres), or roughly the size of Maine - and contains 10 percent of the world's surface fresh water."
This distinct blend of size and richness not only enhances the ecosystem's diversity but also solidifies its status as a crucial natural landmark within the Great Lakes system. The shoreline of Lake Superior measures 1,826 miles (2,938 kilometers), further enhancing its importance as a vital natural resource.
Examine Ecological and Geological Implications
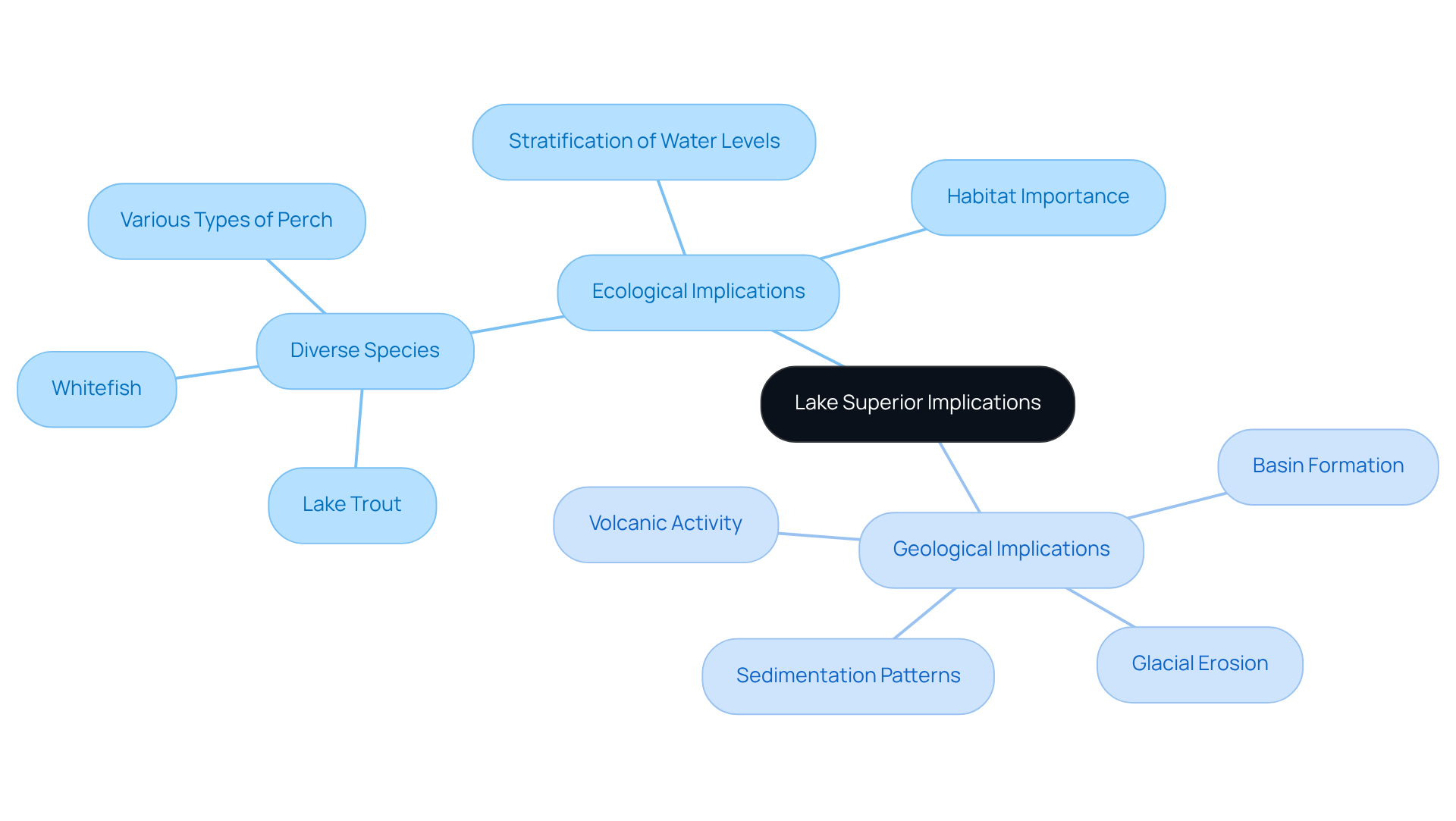
The measurement of the largest freshwater body, Lake Superior, holds significant ecological implications, as it sustains a diverse array of aquatic organisms, including species such as lake trout, whitefish, and various types of perch. The stratification of water levels creates distinct habitats that are crucial for the survival of these species.
Geologically, Lake Superior resides within a basin shaped by ancient volcanic activity and glacial erosion, rendering it a focal point for researchers investigating the Earth's geological history. Furthermore, the depth of Lake Superior map plays a critical role in influencing sedimentation patterns and nutrient cycling, which are essential for preserving the health of its ecosystem.
Understanding these implications is paramount for conservation efforts aimed at safeguarding this unique natural resource.
Conclusion
Lake Superior's depth serves not just as a measurement; it is a defining characteristic that shapes the lake's ecological and geological significance. With an impressive average depth of 500 feet and a maximum of 1,332 feet, Lake Superior emerges as a critical player in the Great Lakes system, influencing everything from temperature stratification to the diverse aquatic life that thrives within its depths.
Key insights explored throughout this article reveal how the unique depth of Lake Superior supports a rich biodiversity, sustains various fish species, and impacts local weather patterns. The historical context surrounding the lake, marked by notable shipwrecks, further underscores the challenges posed by its formidable nature. The geological implications emphasize Lake Superior's role as a vital natural resource, shaped by ancient volcanic activity and glacial processes.
Recognizing the importance of Lake Superior's depth is essential for fostering conservation efforts and ensuring the health of this unique ecosystem. As stewards of such an invaluable resource, it is crucial to appreciate its complexities and advocate for its preservation. Engaging with Lake Superior's ecological narrative not only deepens understanding but also inspires action to protect this remarkable body of water for future generations.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is the average depth of Lake Superior?
The average depth of Lake Superior is approximately 500 feet (152 meters).
What is the maximum depth of Lake Superior?
The maximum depth of Lake Superior is 1,332 feet (406 meters).
How does the depth of Lake Superior affect its water volume?
The depth of Lake Superior contributes to its vast water volume, which is estimated at 2,900 cubic miles (12,100 km³).
What role does Lake Superior's depth play in its ecosystem?
The depth of Lake Superior influences temperature stratification and overall ecosystem health, affecting aquatic life and nutrient distribution.
What types of species are supported by Lake Superior's deep waters?
The cold, deep waters of Lake Superior create a unique habitat that supports diverse species, particularly fish that thrive in cooler temperatures.
What notable wildlife can be found in the regions surrounding Lake Superior?
The areas surrounding Lake Superior, such as Isle Royale National Park, are home to fauna like wolves and moose.
What historical events are associated with Lake Superior?
Lake Superior has a historical context marked by notable shipwreck disasters, highlighting its formidable nature.
Why is Lake Superior significant for ecological research and conservation?
The intricate connection between the depth of Lake Superior and its ecosystem dynamics establishes the area as a vital region for ecological research and conservation initiatives.


