Overview
The article emphasizes the advanced techniques employed to measure Lake Tahoe's depth, underscoring the profound impact this depth has on its ecosystem. Advanced methods, such as multi-beam echosounders, deliver precise depth measurements. These measurements lead to significant thermal stratification, which in turn affects nutrient distribution and oxygen levels—elements crucial for sustaining the health of aquatic life. This connection between measurement techniques and ecological outcomes is vital, illustrating the importance of these methodologies in understanding and preserving Lake Tahoe's unique environment.
Introduction
Nestled amidst the majestic Sierra Nevada mountains, Lake Tahoe stands as a breathtaking testament to nature's beauty and complexity. Renowned for its stunning clarity and remarkable depth, this iconic lake is not only the second deepest in the United States but also a vital ecosystem that supports diverse aquatic life.
As researchers delve into the intricate relationships between the lake's depth and its ecological health, they uncover fascinating insights into:
- Thermal stratification
- Nutrient dynamics
- The impacts of climate change
This exploration reveals the significance of advanced measurement techniques and ongoing environmental efforts aimed at preserving this treasured natural resource for generations to come.
Explore Lake Tahoe: Key Facts and Depth Overview
Lake Tahoe, nestled in the Sierra Nevada mountains, stands out for its stunning clarity and impressive volume. As the second deepest body of water in the United States, Tahoe depth reaches a remarkable maximum of 1,645 feet (501 meters) and features an average depth of approximately 1,000 feet (305 meters). Stretching 22 miles in length and 12 miles in width, it encompasses a surface area of 191 square miles. This extraordinary geological formation, shaped over two million years, not only enhances the area's breathtaking beauty but also plays a crucial role in its ecological health.
The tahoe depth of this body of water profoundly influences its ecosystem. The thermal stratification, resulting from rising temperatures, can impede winter overturn, leading to nutrient accumulation in the surface waters. As noted by the Environmental Research Center in the region, "the resulting thermal stratification from these increased temperatures will serve as a barrier to winter overturn in the body of water and cause nutrients to accumulate in the surface waters, which has the potential to fundamentally alter the physics, chemistry, and biology of this area." This phenomenon presents potential risks to the delicate balance of the water body, impacting its physical, chemical, and biological characteristics.
Since 1980, the Interagency Monitoring Program has been instrumental in monitoring water quality in tributary streams, providing essential data that has informed initiatives aimed at reducing nutrient and sediment influx into the lake. This initiative supports environmental planning and decision-making in the Basin, ensuring the protection of its pristine waters.
Recent updates, including the Greenhouse Gas Inventory for the region published in April 2021, underscore ongoing efforts to address environmental challenges associated with the lake's size and ecology. Understanding these critical aspects of the lake's tahoe depth and ecology is vital for appreciating its environmental significance and the proactive measures necessary to protect this treasured natural asset.
Examine Measurement Techniques for Lake Tahoe's Depth
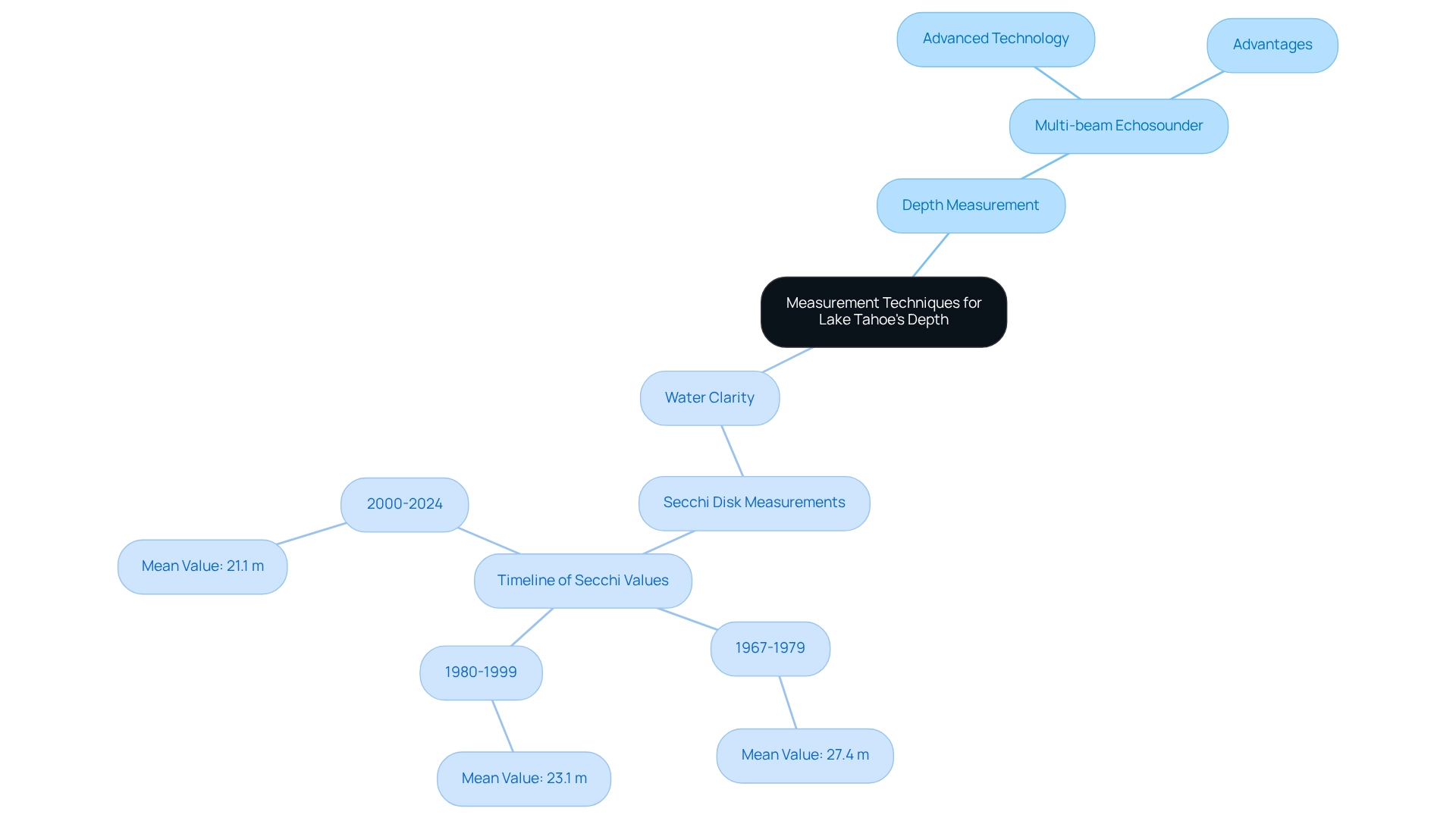
Assessing Tahoe depth employs advanced methods that yield accurate and reliable information. A prominent technique is the multi-beam echosounder, which utilizes sound waves to generate detailed maps of the lake's floor. This technology captures vertical profiles at regular intervals, providing a comprehensive understanding of the lake's bathymetry, including Tahoe depth. As of 2025, the latest advancements in this technology have significantly enhanced measurement precision, establishing it as an indispensable tool for researchers and environmental managers, while Secchi disk measurements are utilized to evaluate water clarity, indirectly indicating Tahoe depth by revealing how light penetrates the water column. The significance of clarity as a measure of water quality and ecosystem health has been highlighted in recent studies. Mean Secchi values have shown a decline from 27.4 meters in 1967-1979 to 21.1 meters from 2000 to 2024, as noted by Ramon C. Naranjo. This trend underscores the necessity for ongoing monitoring and illustrates the impact of seasonal variations on clarity. Research indicates that clarity values can drop significantly during certain months, particularly influenced by winter mixing and spring runoff. A case study titled 'Impact of Seasonal Variations on Water Clarity' examined these interannual variations, emphasizing the need to understand seasonal influences on clarity trends.
These measurement techniques have been standardized since the late 1960s, ensuring consistency in data collection and analysis. The Science Advisory Council has played a pivotal role in coordinating efforts related to clarity reports, emphasizing the need for accurate assessments to inform conservation strategies. In 2023, implementors achieved 98% of the load reduction target, reflecting ongoing environmental efforts that are crucial to water quality. Understanding these methodologies is essential for experts engaged in environmental research and conservation efforts concerning the area surrounding the lake.
Analyze the Impact of Depth on Lake Tahoe's Ecosystem
The tahoe depth significantly influences the ecological dynamics of Lake Tahoe. Deeper bodies of water, such as Tahoe, exhibit thermal stratification, where the Tahoe depth allows for the maintenance of varying temperatures in the water layers throughout the year. This stratification critically affects nutrient distribution and oxygen levels, essential for aquatic life. For instance, the cold, deep waters can become depleted of oxygen, impacting fish populations and other aquatic organisms. Furthermore, the tahoe depth of the water body influences its clarity and the penetration of sunlight, which in turn affects photosynthesis in aquatic plants.
Research indicates that since 2005, water temperature profiles have been meticulously measured, serving as indicators of climate change. These measurements reveal how thermal dynamics are shifting, with profound implications; as temperatures rise, the mixing patterns of the body of water are altered, potentially leading to lower dissolved oxygen levels that threaten the viability of coldwater fish species. Case studies examining the impacts of climate change on Lake Tahoe's salmonid populations highlight the risks associated with these changing thermal and mixing dynamics. These studies indicate that rising temperatures might worsen oxygen depletion, further jeopardizing the fragile balance of the aquatic ecosystem.
As Mark Twain famously noted, "It blows flimsy houses down, lifts shingle roofs occasionally, rolls up tin ones like sheet music..." This quote reflects the unpredictable nature of the area’s environment. Understanding these ecological impacts is essential for developing effective conservation strategies that ensure the health and sustainability of Lake Tahoe's unique ecosystem, especially in light of the profound effects of continued atmospheric warming on lake ecosystems worldwide.
Conclusion
The intricate relationship between Lake Tahoe's depth and its ecological health illustrates nature's delicate balance. The lake's remarkable depth of 1,645 feet not only enhances its breathtaking beauty but also plays a crucial role in its thermal stratification, nutrient dynamics, and overall ecosystem health. Ongoing monitoring efforts, such as those undertaken by the Lake Tahoe Interagency Monitoring Program, are essential for understanding the impacts of these factors and safeguarding the lake's pristine waters.
Advanced measurement techniques, including multi-beam echosounders and Secchi disk assessments, have proven vital in providing accurate data on the lake's depth and clarity. This data informs researchers and guides environmental management strategies aimed at mitigating the effects of climate change and preserving the lake's delicate ecosystem. The alarming trends in water clarity and temperature profiles underscore the urgency of these efforts.
Ultimately, preserving Lake Tahoe's ecological integrity is paramount, as its health is intrinsically linked to the broader environmental challenges faced by freshwater ecosystems worldwide. By fostering an understanding of the lake's unique characteristics and the pressing need for conservation, stakeholders can collaborate to ensure that this natural treasure remains a vibrant and resilient ecosystem for generations to come.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is the depth of Lake Tahoe?
Lake Tahoe has a maximum depth of 1,645 feet (501 meters) and an average depth of approximately 1,000 feet (305 meters).
How large is Lake Tahoe?
Lake Tahoe stretches 22 miles in length and 12 miles in width, encompassing a surface area of 191 square miles.
How was Lake Tahoe formed?
Lake Tahoe is an extraordinary geological formation shaped over two million years.
What impact does the depth of Lake Tahoe have on its ecosystem?
The depth influences thermal stratification, which can impede winter overturn and lead to nutrient accumulation in the surface waters, potentially altering the lake's physical, chemical, and biological characteristics.
What monitoring efforts have been undertaken to protect Lake Tahoe's water quality?
Since 1980, the Interagency Monitoring Program has monitored water quality in tributary streams, providing essential data to reduce nutrient and sediment influx into the lake.
What recent initiatives have been introduced to address environmental challenges in the Lake Tahoe region?
Recent updates include the Greenhouse Gas Inventory published in April 2021, which highlights ongoing efforts to tackle environmental challenges associated with the lake's size and ecology.
Why is understanding Lake Tahoe's depth and ecology important?
Understanding these aspects is vital for appreciating the lake's environmental significance and the proactive measures necessary to protect this treasured natural asset.



