Overview
The article emphasizes the remarkable size, depth, and historical significance of Lake Tahoe, showcasing its unique geographical features and vital ecological role. Lake Tahoe spans approximately 191 square miles and reaches an impressive maximum depth of 1,645 feet. However, it faces significant ecological challenges due to human activities. This situation underscores the urgent need for ongoing conservation efforts to preserve its health and clarity, inviting stakeholders to take action in safeguarding this natural treasure.
Introduction
Lake Tahoe, a stunning alpine lake nestled in the Sierra Nevada, stands as a visual marvel and a critical ecological resource. Spanning 191 square miles, it is North America's largest alpine body of water, with a depth that profoundly influences its unique ecosystems and water clarity. However, as human activities and climate change increasingly threaten its pristine environment, understanding the lake's dimensions, historical context, and current conservation efforts has become essential.
What challenges lie ahead for this iconic natural treasure? Awareness and action can help preserve its beauty for generations to come.
Explore Lake Tahoe's Geography and Ecology
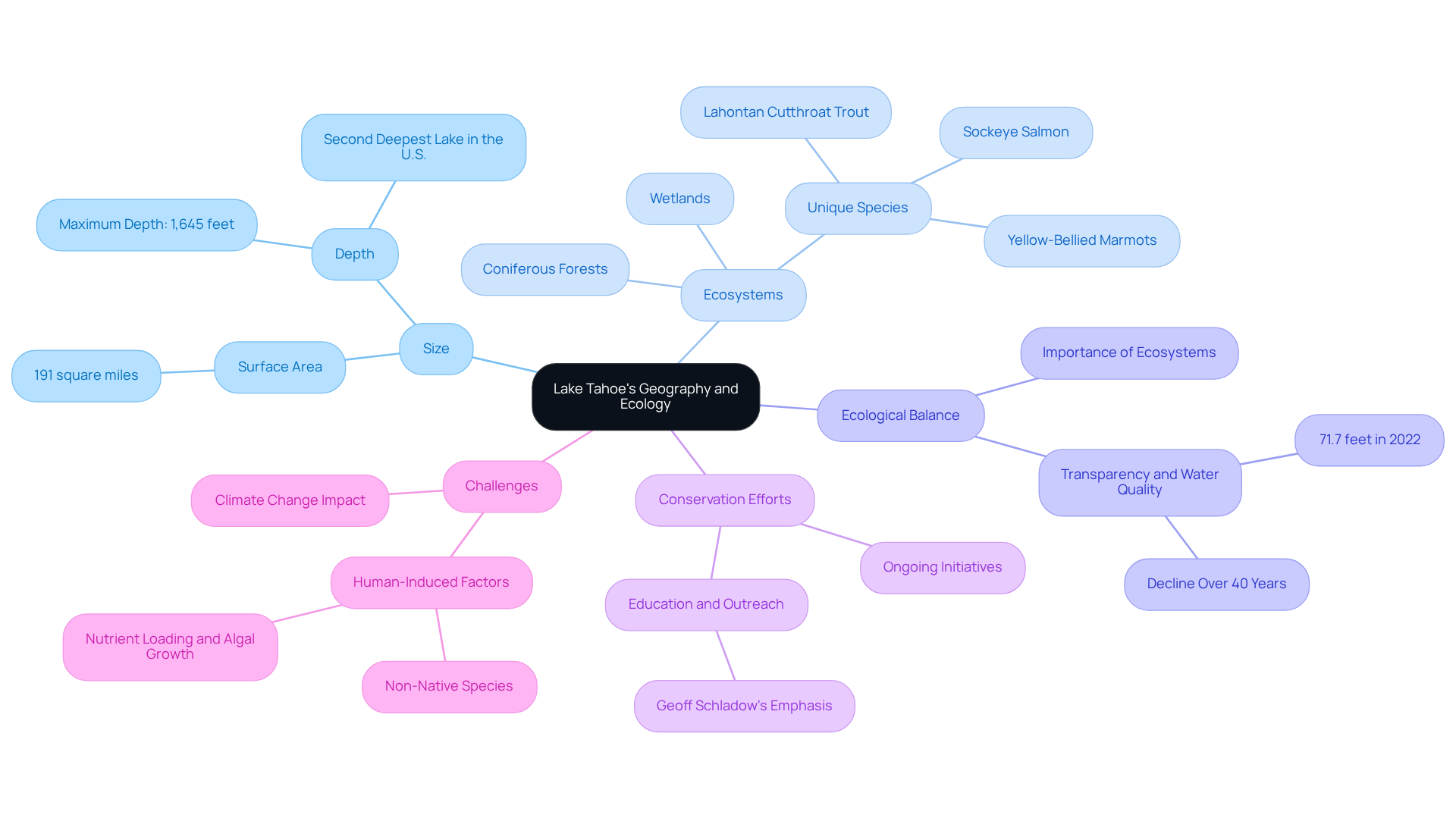
Lake Tahoe, a jewel nestled in the Sierra Nevada mountain range along the California-Nevada border, is renowned for its breathtaking blue waters and majestic mountainous backdrop. Spanning approximately 191 square miles, the lake has a lake Tahoe size, making it the largest alpine body of water in North America. This extraordinary area showcases a diverse array of ecosystems, including coniferous forests, wetlands, and numerous unique species, all of which are crucial for maintaining the aquatic ecological balance. Such balance is essential, as it sustains various species and significantly contributes to the lake's renowned transparency and overall health. The watershed of Lake Tahoe encompasses 501 square miles, playing a vital role in preserving water quality and ecological integrity.
Recent ecological impact studies underscore the significance of these ecosystems, revealing their interactions with human activities and climate change. Notably, the transparency of this alpine lake reached an impressive 71.7 feet in 2022, highlighting the success of ongoing conservation initiatives. Nevertheless, challenges remain, including the introduction of non-native species and the decline in water clarity over the past 40 years due to human-induced factors.
Conservation efforts continue to focus on safeguarding this essential resource and ensuring its sustainability for future generations. As Geoff Schladow, Director of TERC, emphasizes, education and outreach are paramount in promoting responsible action and stewardship for the area's ecosystem.
Analyze Lake Tahoe's Dimensions and Depth
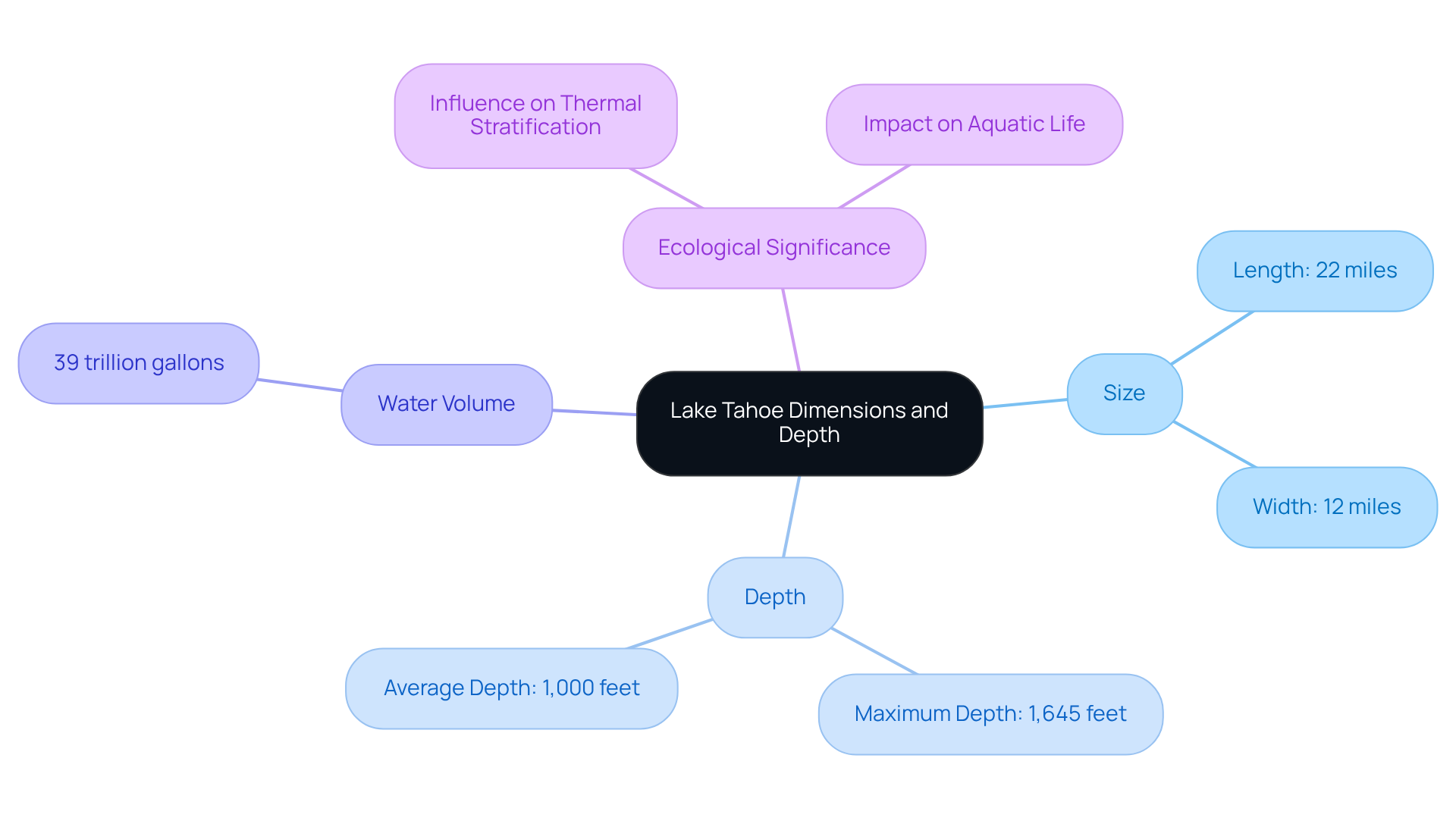
The lake Tahoe size spans approximately 22 miles in length and 12 miles in width, with a maximum depth of 1,645 feet, making it the second-deepest body of water in the United States, following Crater Lake. Its average depth is around 1,000 feet. This impressive depth plays a crucial role in the body of water's thermal stratification, significantly influencing its ecology and water clarity.
Holding approximately 39 trillion gallons of water, the large lake serves as a vital resource for surrounding communities and ecosystems. Understanding these dimensions is essential for appreciating the lake's impact on regional hydrology and its capacity to sustain diverse aquatic life, particularly when considering the lake tahoe size.
Furthermore, the emotional bond that individuals and businesses have with this area makes it a significant location for meaningful gifts. At Pangea Maps, we celebrate these connections through our personalized handcrafted 3D maps. Each map is meticulously hand sketched over bathymetry, crafted from the highest grade 1.5mm birch ply topped with white acrylic, and framed locally using environmentally sourced materials.
The custom designs take roughly an hour to create, transforming them into not only gifts but also treasured memories that celebrate the beauty and importance of locations such as the lake region.
Examine Historical Perspectives on Lake Tahoe's Size
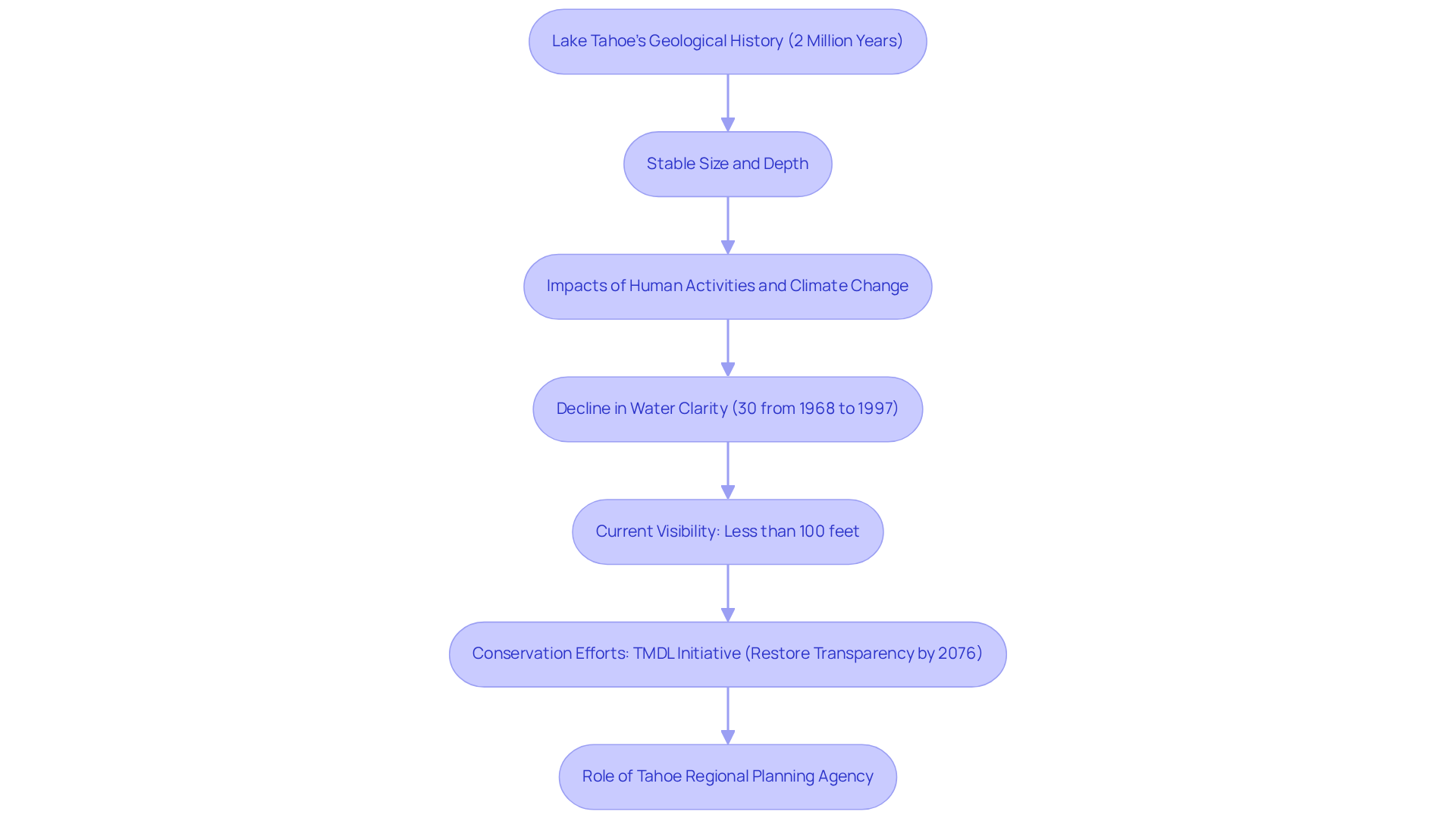
Lake Tahoe boasts a geological history that spans approximately two million years, having been shaped during the last Ice Age. Although the lake's size and depth have remained relatively stable, its transparency and ecological health have been significantly impacted by human activities and climate change.
Historical records indicate that visibility in the lake once exceeded 100 feet, starkly contrasting with current conditions. Urban development, pollution, and increased sedimentation have led to a notable decline in water clarity, with deep-water clarity decreasing by about 30% from 1968 to 1997. This body of water is designated as an Outstanding National Resource Water under the federal Clean Water Act, underscoring its ecological significance.
Urgent conservation efforts are in progress, including the Total Maximum Daily Load (TMDL) initiative, which aims to restore deep-water transparency to 29.7 meters by 2076. Such initiatives emphasize the importance of understanding historical changes to foster effective environmental stewardship.
Furthermore, the lake is fed by 63 streams, with only the Truckee River flowing out, presenting additional challenges due to human activities. The role of the Tahoe Regional Planning Agency in safeguarding the lake through land-use regulation is crucial to these conservation strategies.
Conclusion
Lake Tahoe stands as a remarkable natural wonder, celebrated not only for its stunning beauty but also for its significant ecological and historical importance. This alpine lake, the largest of its kind in North America, plays a crucial role in sustaining diverse ecosystems and maintaining water quality. Understanding Lake Tahoe's geography, size, and depth reveals the intricate balance of nature that is vital to its health and the surrounding communities.
Key insights into Lake Tahoe's dimensions, including its impressive depth of 1,645 feet and vast water volume, highlight its vital role in regional hydrology. Ongoing conservation efforts, the impact of climate change, and the historical decline in water clarity underscore the urgent need for stewardship and education. The lake's rich geological history and the challenges it faces due to human activities further emphasize the importance of preserving this invaluable resource for future generations.
As our understanding of Lake Tahoe's ecological significance deepens, it becomes increasingly clear that collective action is necessary to safeguard its health. Engaging in responsible practices and supporting conservation initiatives will ensure that this precious alpine lake continues to thrive. The beauty and ecological integrity of Lake Tahoe are not just a local treasure; they represent a vital part of our shared environmental heritage that must be cherished and protected.
Frequently Asked Questions
Where is Lake Tahoe located?
Lake Tahoe is located in the Sierra Nevada mountain range along the California-Nevada border.
What is the size of Lake Tahoe?
Lake Tahoe spans approximately 191 square miles, making it the largest alpine body of water in North America.
What types of ecosystems can be found around Lake Tahoe?
The area around Lake Tahoe showcases a diverse array of ecosystems, including coniferous forests, wetlands, and various unique species.
Why is the ecological balance around Lake Tahoe important?
The ecological balance is crucial for sustaining various species and significantly contributes to the lake's renowned transparency and overall health.
What is the size of Lake Tahoe's watershed?
The watershed of Lake Tahoe encompasses 501 square miles and plays a vital role in preserving water quality and ecological integrity.
What recent studies have been conducted regarding Lake Tahoe's ecology?
Recent ecological impact studies have highlighted the interactions between local ecosystems, human activities, and climate change.
What was the transparency level of Lake Tahoe in 2022?
The transparency of Lake Tahoe reached an impressive 71.7 feet in 2022, indicating the success of ongoing conservation initiatives.
What challenges does Lake Tahoe face concerning its ecology?
Challenges include the introduction of non-native species and a decline in water clarity over the past 40 years due to human-induced factors.
What are the goals of conservation efforts at Lake Tahoe?
Conservation efforts aim to safeguard the lake's resources and ensure its sustainability for future generations.
What role does education play in the conservation of Lake Tahoe?
Education and outreach are essential in promoting responsible action and stewardship for the area's ecosystem, as emphasized by Geoff Schladow, Director of TERC.



