Overview
Lake Superior stands as the largest freshwater body in the world by surface area, encompassing approximately 31,700 square miles and containing about 10% of the world's fresh surface water. Its significance is underscored not only by its immense size and volume—ranking third globally in freshwater capacity—but also by its critical ecological and economic roles. This remarkable lake supports diverse wildlife and bolsters local economies through:
- Shipping
- Tourism
- Recreation
This highlights the need for continued awareness and preservation efforts.
Introduction
Lake Superior, the largest freshwater lake by surface area in the world, commands attention with its staggering dimensions and ecological significance. Covering approximately 31,700 square miles and holding about 10% of the planet's fresh surface water, this colossal body of water is not only a vital resource but also a key player in the hydrological systems of North America.
However, as the lake faces increasing environmental pressures and economic demands, one must ponder: how can society balance the need for development with the imperative to preserve such a crucial natural treasure?
Define Lake Superior's Size and Volume
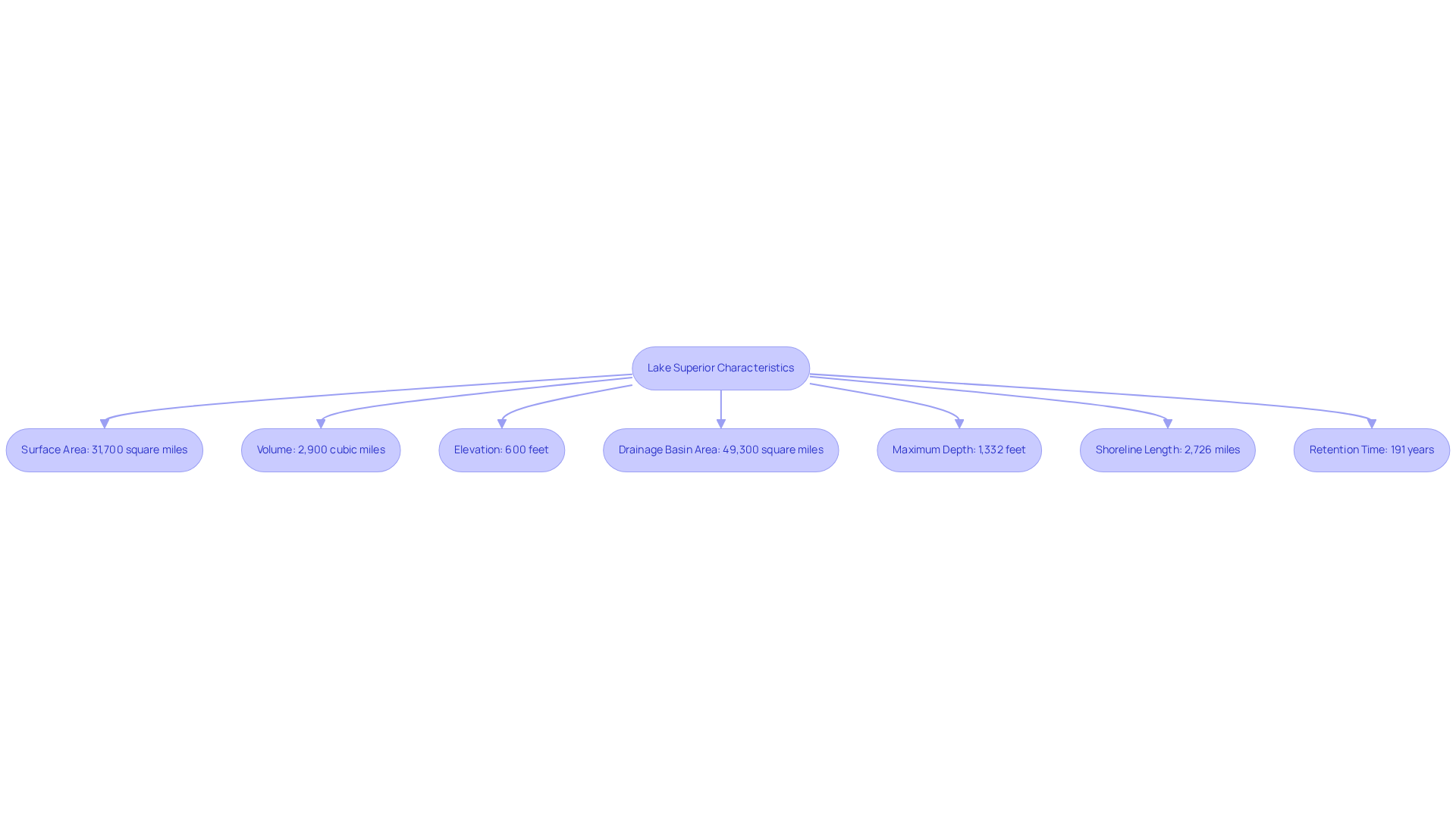
Lake Superior size makes it the largest freshwater body on the planet by surface area, encompassing roughly 31,700 square miles (82,100 square kilometers). This immense lake holds about 10% of the world's fresh surface water, marking it as a critical resource. In terms of volume, Lake Superior ranks as the third-largest freshwater body worldwide, boasting an estimated capacity of 2,900 cubic miles (12,100 cubic kilometers).
With an elevation of 600 feet (183 meters) and a drainage basin area of 49,300 square miles (127,700 square kilometers), its characteristics are truly remarkable. The maximum depth reaches 1,332 feet (406 meters), while the shoreline stretches approximately 2,726 miles (4,385 kilometers).
The lake superior size, with its vast dimensions, not only highlights its significance as a natural resource but also establishes it as a prominent geographical landmark in North America. The lake's cold, clear waters nurture a diverse range of native fish species, and its extensive watershed, primarily influenced by the Canadian Shield, contributes to its unique ecological attributes.
Furthermore, with a retention time of 191 years, Lake Superior plays a vital role in hydrology and ecological dynamics, underscoring its importance in the region.
Examine Geographical Context and Comparisons
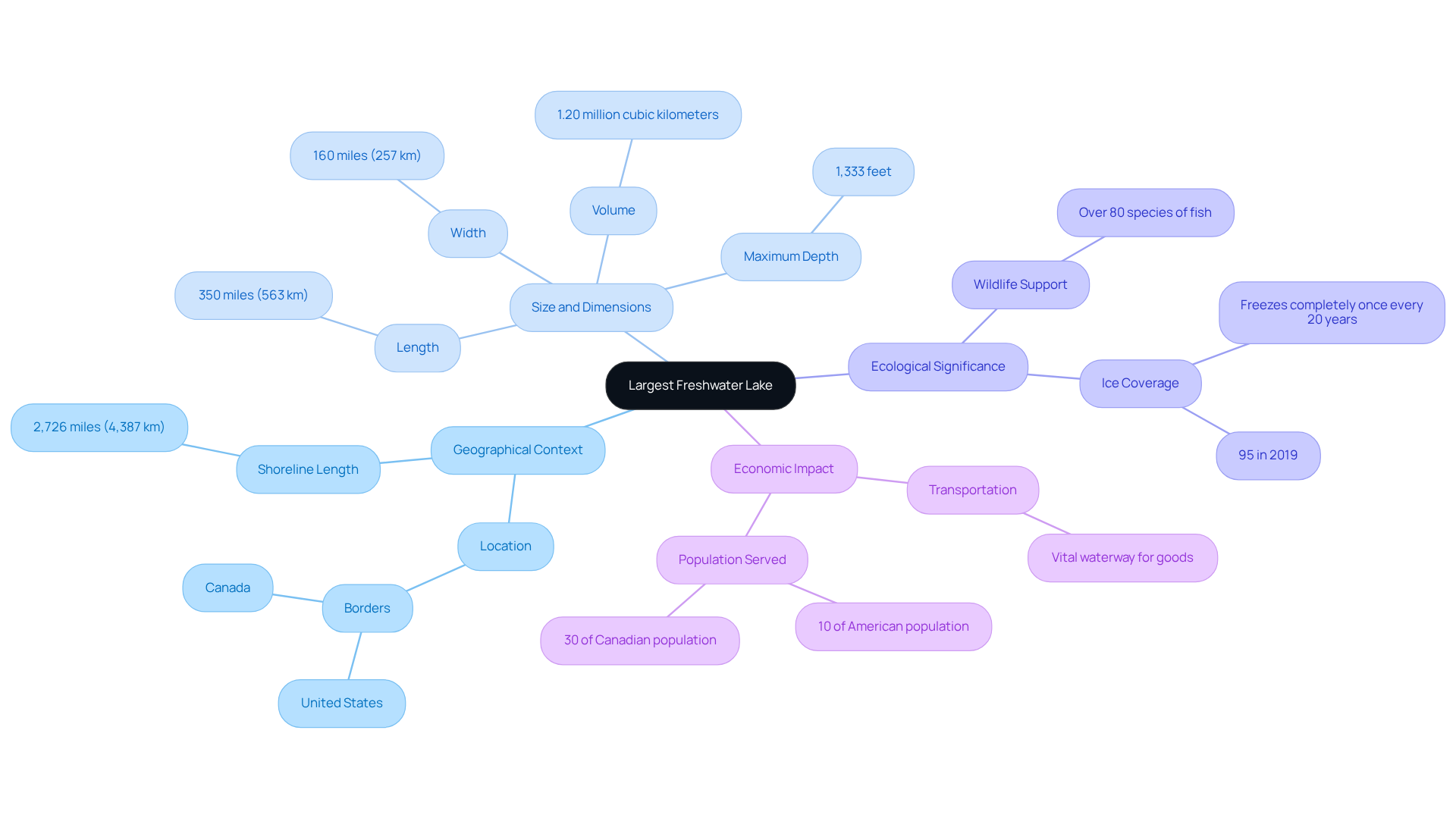
The largest freshwater lake straddles the border between the United States and Canada, bordered by Minnesota, Wisconsin, Michigan's Upper Peninsula, and Ontario. Its vast dimensions are striking, reflecting a lake superior size that extends approximately 350 miles (563 kilometers) in length and 160 miles (257 kilometers) in width. This makes it larger than South Carolina and comparable in size to Austria, reflecting the lake superior size. The lake holds an impressive volume of 1.20 million cubic kilometers and reaches a maximum depth of 1,333 feet, underscoring its significance in the Great Lakes system.
Such geographical positioning establishes it as a crucial waterway for transportation and commerce while highlighting its role as a significant ecological zone, supporting diverse wildlife and habitats. Notably, the largest freshwater lake in North America freezes entirely once every 20 years, with its ice coverage reaching 95% in 2019, reflecting its climatic conditions. The Great Lakes system serves approximately 10% of the American population and 30% of the Canadian population, emphasizing the economic influence of this vast body of water on the surrounding areas.
Analyze Ecological and Economic Significance
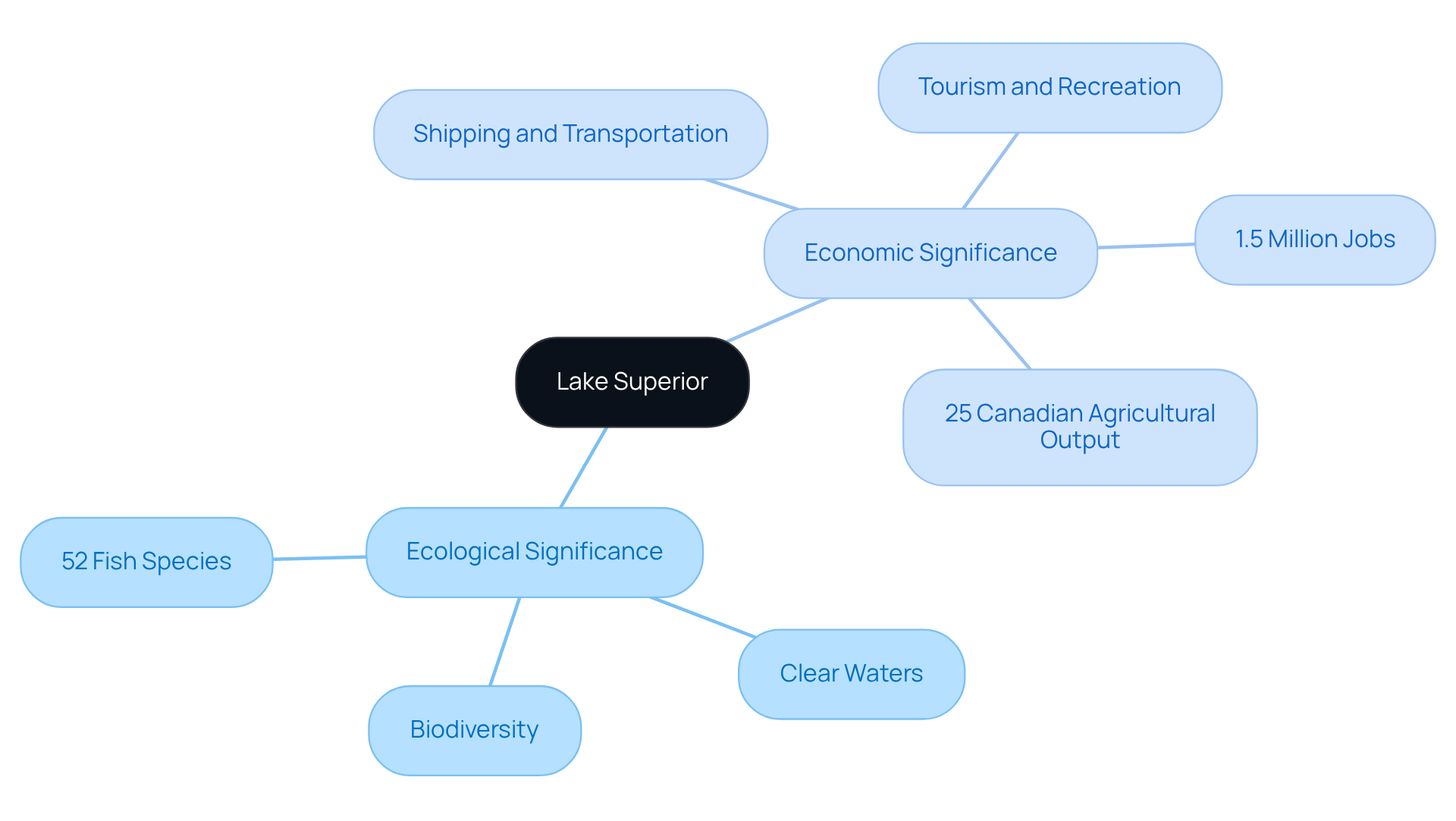
Lake Superior stands as a cornerstone of both ecological health and economic vitality in the region. Its ecological significance is underscored by the presence of 52 fish species—fewer than any other Great Body of Water—making it a critical habitat for a diverse array of birds and wildlife. The lake's oligotrophic nature, characterized by low nutrient levels, results in remarkably clear waters and unique ecosystems, which are essential for maintaining biodiversity.
Economically, this vast freshwater lake is indispensable for shipping and transportation, facilitating the movement of vital goods such as iron ore and grain. Surrounding communities reap substantial benefits from tourism, fishing, and recreational activities, all integral to the local economy. Notably, the Great Lakes region, including Lake Superior, supports over 1.5 million jobs and generates billions in economic activity annually.
The significant role of Duluth, Minnesota, as a commercial shipping hub further illustrates this impact, exporting agricultural products and contributing to the region's economic resilience. Furthermore, nearly 25% of Canadian agricultural output occurs within the Great Lakes region, highlighting its crucial role in supporting local economies. The lake's resources are vital for local fisheries, which not only sustain livelihoods but also enhance community identity and cultural heritage.
Consequently, the economic, ecological significance, and Lake Superior's size are profound, underscoring the urgent need for sustainable practices to protect this invaluable resource.
Conclusion
Lake Superior's immense size and significance cannot be overstated; it stands as the largest freshwater lake by surface area in the world. This remarkable body of water holds a staggering 10% of the planet's fresh surface water and plays a crucial role in the ecological and economic landscapes of North America. Its vast dimensions and unique characteristics establish Lake Superior as a vital resource that warrants attention and protection.
The article highlights several key aspects of Lake Superior, including:
- Its impressive size
- Geographical context
- Ecological and economic importance
With a surface area of approximately 31,700 square miles and a maximum depth of 1,332 feet, Lake Superior is larger than many countries and serves as a critical habitat for diverse wildlife. Additionally, its economic contributions are significant, supporting millions of jobs and facilitating vital shipping routes that enhance local economies.
Reflecting on the importance of Lake Superior, it becomes clear that sustainable practices are essential to preserving this invaluable resource for future generations. As the lake continues to influence the surrounding ecosystems and economies, understanding its dimensions and significance serves as a call to action for conservation efforts. Protecting Lake Superior is crucial not only for maintaining biodiversity but also for ensuring the prosperity of the communities that rely on its resources.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is the surface area of Lake Superior?
Lake Superior has a surface area of approximately 31,700 square miles (82,100 square kilometers), making it the largest freshwater body on the planet by surface area.
How much of the world's fresh surface water does Lake Superior hold?
Lake Superior holds about 10% of the world's fresh surface water.
Where does Lake Superior rank in terms of volume among freshwater bodies?
Lake Superior ranks as the third-largest freshwater body worldwide in terms of volume, with an estimated capacity of 2,900 cubic miles (12,100 cubic kilometers).
What is the maximum depth of Lake Superior?
The maximum depth of Lake Superior is 1,332 feet (406 meters).
How long is the shoreline of Lake Superior?
The shoreline of Lake Superior stretches approximately 2,726 miles (4,385 kilometers).
What is the elevation of Lake Superior?
Lake Superior has an elevation of 600 feet (183 meters).
What is the drainage basin area of Lake Superior?
The drainage basin area of Lake Superior is 49,300 square miles (127,700 square kilometers).
What ecological significance does Lake Superior have?
Lake Superior's cold, clear waters support a diverse range of native fish species, and its extensive watershed contributes to its unique ecological attributes.
What is the retention time of water in Lake Superior?
The retention time of water in Lake Superior is 191 years, highlighting its role in hydrology and ecological dynamics.



