Overview
Lake Superior's maximum depth of 1,333 feet (406 meters) stands as a cornerstone for its ecological health and navigational safety. This remarkable depth supports a diverse array of aquatic life and facilitates safe maritime operations.
It is crucial to note that this depth significantly influences temperature stratification, which in turn benefits fish populations. Moreover, it plays a vital role in pollution management and enhances the stability of navigation.
Thus, Lake Superior is underscored as an essential freshwater resource in North America.
Introduction
Lake Superior stands as a monumental freshwater body, not only due to its vast surface area but also because of its extraordinary depth, reaching a staggering 1,333 feet. This depth is not merely a statistic; it plays a pivotal role in sustaining the lake's rich biodiversity and ecological health, influencing everything from temperature stratification to aquatic life.
As the significance of such measurements becomes increasingly evident, questions arise regarding how this depth impacts navigational safety and pollution management. What are the broader implications of Lake Superior's profound depths for both its ecosystem and the communities that depend on it?
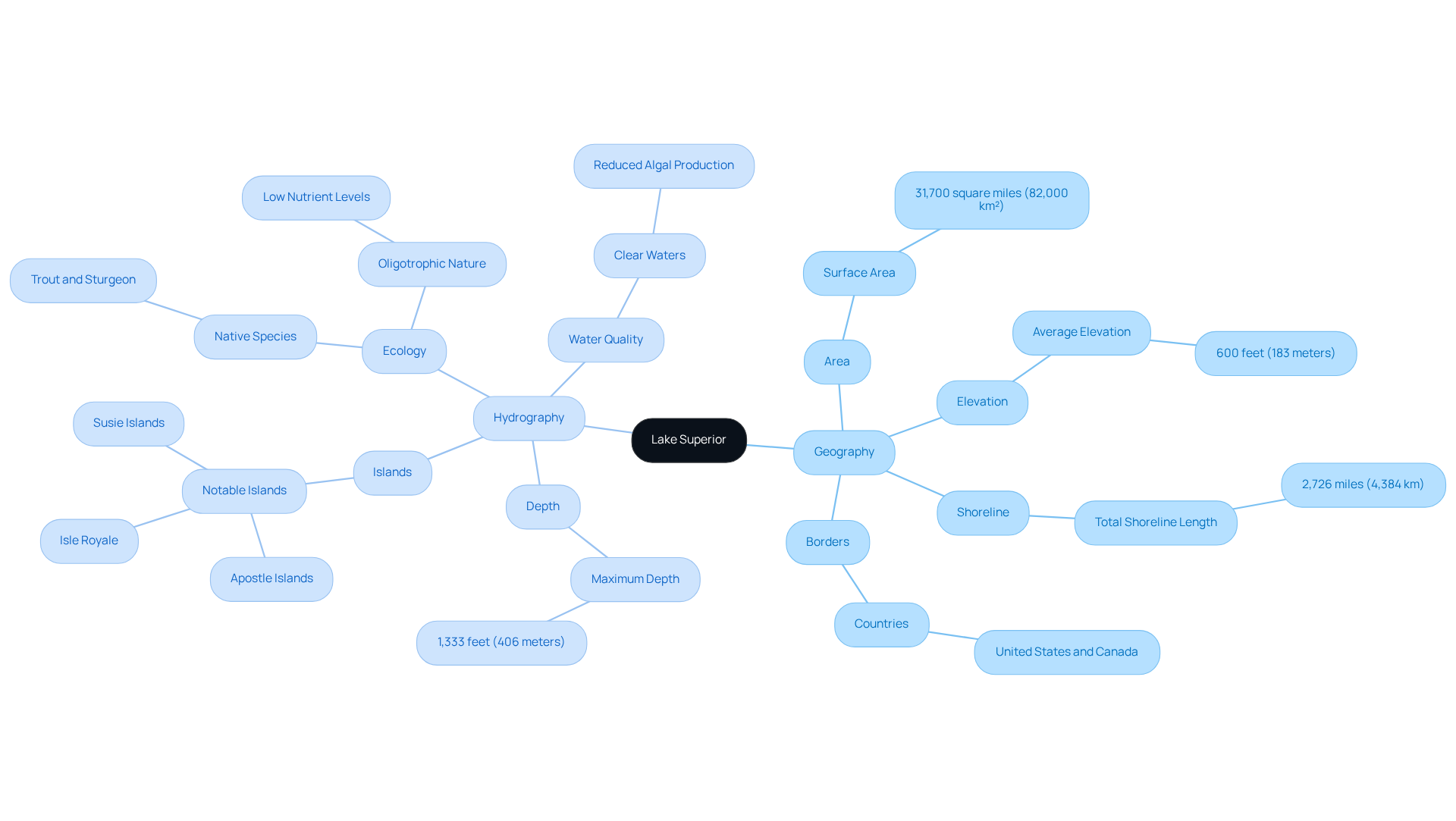
Explore Lake Superior: Geography and Hydrography
Lake Superior, the largest freshwater body recognized globally by surface area, spans approximately 31,700 square miles (82,100 square kilometers) and is bordered by both the United States and Canada, extending into Ontario at its northernmost point. Its average elevation is about 600 feet (183 meters) above sea level, complemented by a shoreline that measures around 2,726 miles (4,384 kilometers), highlighting its significance in North America's geography.
The hydrography of Lake Superior is characterized by deep basins and numerous islands, which are essential to its unique ecosystem and hydrological dynamics. The depth of Lake Superior varies significantly, with the lake superior maximum depth reaching 1,333 feet (406 meters), making it the most profound of the Great Lakes. This notable depth is vital for the lake's ecology, influencing temperature stratification and supporting diverse aquatic life, including native species such as trout and sturgeon.
Recent studies underscore the critical role of Lake Superior's surface area and shoreline in sustaining ecological balance and bolstering local fisheries. The lake's oligotrophic nature, marked by low nutrient levels, contributes to its clear waters and reduced algal production compared to other Great Lakes. Experts assert that the unique hydrographic features of this water body, including its volume of 2,900 cubic miles (12,000 cubic kilometers), are pivotal in regional climate regulation and water management practices.
In conclusion, the geographical and hydrographic characteristics of Lake Superior not only define its ecological importance but also enhance its status as a vital freshwater resource in North America.
Analyze Lake Superior's Depth: Key Measurements and Comparisons
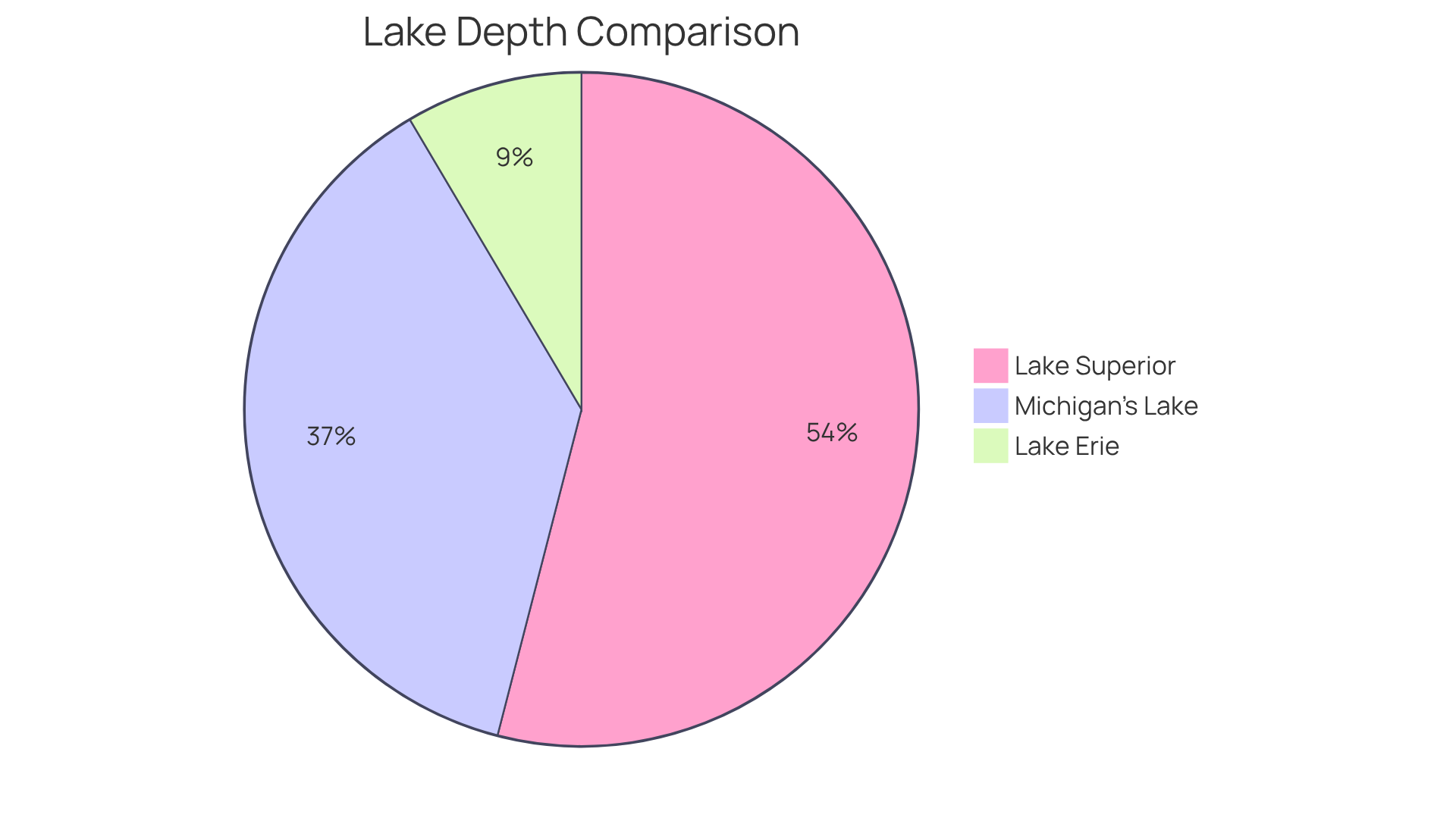
Lake Superior, known for its impressive average depth of approximately 483 feet (147 meters), reaches a maximum depth of 1,333 feet (406 meters), making it the deepest of the Great Lakes and one of the most profound water bodies globally. Furthermore, it holds the title of the largest freshwater lake in the world by surface area, encompassing 31,700 square miles (82,100 square kilometers).
In comparison:
- Michigan's largest water body attains a maximum depth of 925 feet (282 meters).
- Lake Erie, the shallowest of the Great Lakes, measures only 210 feet (64 meters) at its deepest point.
This remarkable depth significantly contributes to the immense volume of the water body, estimated at 2,900 cubic miles (12,100 cubic kilometers). Such volume plays a crucial role in sustaining diverse aquatic ecosystems and maintaining high water quality. The cold waters of this vast freshwater lake inhibit bacterial growth, further enhancing its ecological health.
Recent environmental research underscores the importance of these measurements, as they are vital for navigation, recreational activities, and understanding the ecological dynamics of the water body. Moreover, this expansive freshwater lake supports substantial economic activities, including shipping, tourism, and recreation, which are essential for the surrounding communities. The profundity of this largest freshwater body not only sustains a rich variety of life but also influences the water's thermal dynamics, crucial for the overall health of the Great Lakes ecosystem.
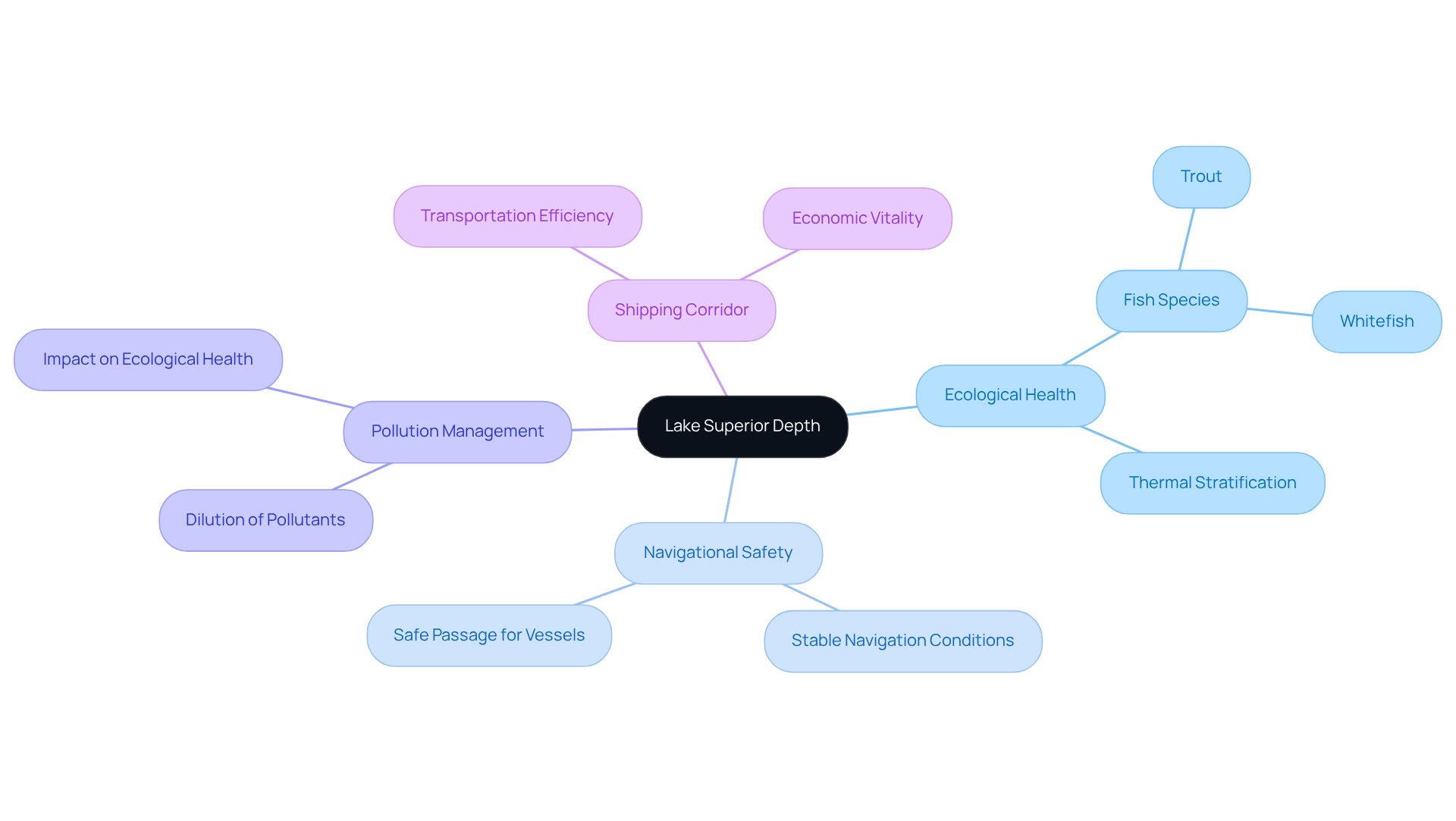
Examine the Ecological and Navigational Importance of Depth
The significance of Lake Superior's maximum depth, the largest freshwater body in North America, cannot be overstated; its profound depth is a critical factor influencing both ecological health and navigational safety. The stratified layers of water create distinct thermal zones that foster a variety of fish species, such as trout and whitefish, which flourish in the cold, deep waters. This measurement is essential not only for sustaining these aquatic populations but also for facilitating the safe passage of large vessels, establishing this body of water as a crucial shipping and transportation corridor.
Furthermore, the considerable depth of the lake plays a vital role in pollution management; deeper regions can dilute pollutants more effectively than shallower areas, thereby reducing their ecological impact. Recent studies on navigational safety have underscored that the volume of Lake Superior, influenced by the lake superior maximum depth, enhances maritime operations' safety, as deeper lakes typically provide more stable navigation conditions.
Experts assert that comprehending the relationship between depth and navigational safety is imperative for sustainable management and conservation efforts, ensuring this essential freshwater resource continues to bolster both ecological diversity and economic vitality.
Conclusion
Lake Superior's maximum depth is a defining characteristic that underscores its ecological and navigational significance. Recognized as the largest freshwater body by surface area, the lake reaches a remarkable depth of 1,333 feet, making it not only the deepest of the Great Lakes but also a vital resource for local ecosystems and economic activities. This profound depth plays a crucial role in maintaining the lake's unique thermal dynamics, supporting diverse aquatic life, and ensuring safe navigation for vessels traversing its waters.
Key insights throughout the article highlight the importance of Lake Superior's depth in various contexts. The hydrographic features of this expansive body of water contribute to its ecological health, facilitating the growth of cold-water species and enhancing water quality. Furthermore, the lake's depth aids in pollution management and provides stability for maritime operations, essential for the surrounding communities' economic well-being. Comparisons with other Great Lakes further emphasize Lake Superior's unparalleled stature in terms of depth and volume, reinforcing its role as a critical freshwater resource.
In light of these insights, recognizing the broader implications of Lake Superior's maximum depth is imperative. As environmental challenges continue to evolve, understanding the relationship between depth, ecology, and navigation becomes increasingly vital for sustainable management and conservation efforts. Protecting this unique water body not only ensures the survival of its diverse ecosystems but also supports the economic activities that depend on its vast resources. Emphasizing the significance of Lake Superior's depth is essential for fostering awareness and encouraging responsible stewardship of this invaluable freshwater treasure.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is Lake Superior known for?
Lake Superior is recognized as the largest freshwater body in the world by surface area, spanning approximately 31,700 square miles (82,100 square kilometers).
Which countries border Lake Superior?
Lake Superior is bordered by both the United States and Canada, extending into Ontario at its northernmost point.
What is the average elevation of Lake Superior?
The average elevation of Lake Superior is about 600 feet (183 meters) above sea level.
How long is the shoreline of Lake Superior?
The shoreline of Lake Superior measures around 2,726 miles (4,384 kilometers).
What are the key hydrographic features of Lake Superior?
Lake Superior is characterized by deep basins, numerous islands, and a maximum depth of 1,333 feet (406 meters), which is the deepest of the Great Lakes.
How does the depth of Lake Superior affect its ecology?
The depth of Lake Superior influences temperature stratification and supports diverse aquatic life, including native species such as trout and sturgeon.
What is the significance of Lake Superior's oligotrophic nature?
Lake Superior's oligotrophic nature, marked by low nutrient levels, contributes to its clear waters and reduces algal production compared to other Great Lakes.
What is the volume of Lake Superior?
The volume of Lake Superior is approximately 2,900 cubic miles (12,000 cubic kilometers).
How does Lake Superior contribute to regional climate regulation?
The unique hydrographic features of Lake Superior, including its volume and depth, play a pivotal role in regional climate regulation and water management practices.
Why is Lake Superior considered a vital freshwater resource?
The geographical and hydrographic characteristics of Lake Superior define its ecological importance and enhance its status as a vital freshwater resource in North America.



