Overview
Lake Superior stands as the largest of the Great Lakes by surface area, encompassing approximately 31,700 square miles. It also claims the title of the deepest, reaching a maximum depth of 1,332 feet, factors that significantly shape its unique ecosystem. These impressive dimensions not only bolster its role as a critical freshwater resource, containing about 10 percent of the world's surface freshwater, but they also influence local climate patterns and biodiversity. This reality underscores the urgent need for concerted conservation efforts.
Introduction
The impressive dimensions of Lake Superior establish it as the largest freshwater lake by surface area, revealing a complex ecological tapestry that is vital for both regional biodiversity and global freshwater resources. Spanning an expansive area of 31,700 square miles and reaching a maximum depth of 1,332 feet, this remarkable body of water plays a pivotal role in shaping local climates and sustaining diverse aquatic life.
However, as climate change accelerates, the ecological balance of Lake Superior faces unprecedented challenges. This situation raises critical questions about the future of this essential ecosystem:
- How will the interplay of its dimensions and environmental pressures affect its health?
Explore the Geographical and Hydrological Features of Lake Superior
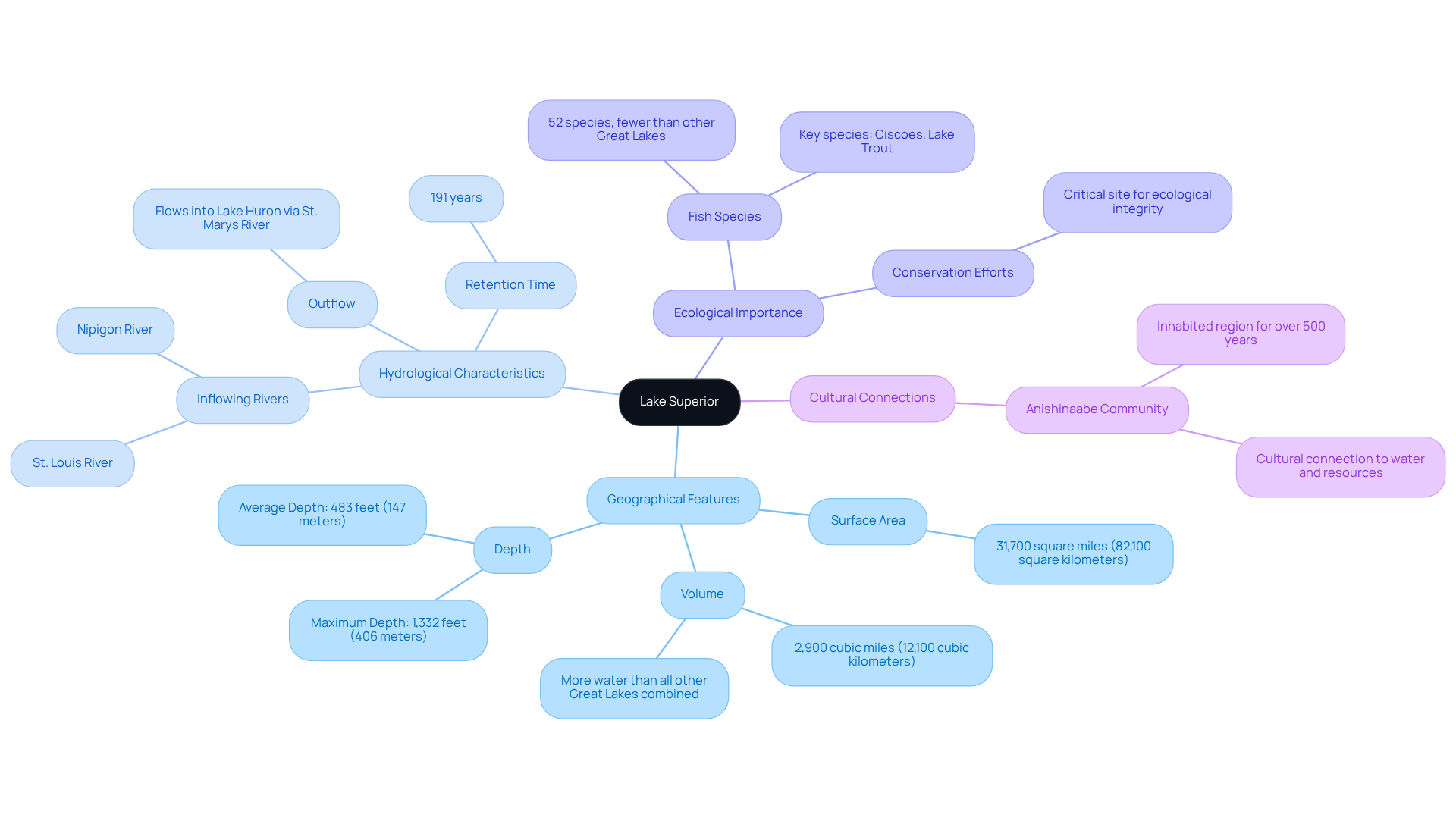
Lake Superior dimensions make it the largest of the Great Lakes by surface area, spanning approximately 31,700 square miles (82,100 square kilometers) and possessing a volume greater than that of all the other Great Lakes combined. This remarkable body of water is bordered by both the United States and Canada, featuring major cities such as Duluth, Minnesota, and Thunder Bay, Ontario, along its shores. Fed by various rivers, including the St. Louis River and the Nipigon River, it flows into Lake Huron through the St. Marys River.
The hydrological characteristics of Lake Superior comprise a complex system of inflows and outflows, crucial for regulating its levels and maintaining ecological balance. With a maximum depth of 1,332 feet (406 meters), the lake superior dimensions not only highlight its status as the largest by surface area but also as the deepest of the Great Lakes, contributing to its unique ecosystem. Recent studies reveal a retention time of 191 years, indicating a slow turnover of its waters, which supports a diverse range of aquatic life while presenting challenges for quality management.
Notably, the cold, clear waters host 52 fish species, fewer than any other Great Lake, due to its unique hydrological traits and limited habitats. This intricate aquatic system plays a vital role in preserving the ecological integrity of the area, making Lake Superior a critical site for both conservation initiatives and recreational activities. Additionally, the Anishinaabe community has inhabited the region surrounding this great body of water for over 500 years, fostering a profound cultural connection to the water and its resources. Hydrologists emphasize the importance of this aquatic system in sustaining the ecosystem's equilibrium, reinforcing the necessity for ongoing conservation efforts.
Analyze the Dimensions: Area, Depth, and Volume of Lake Superior
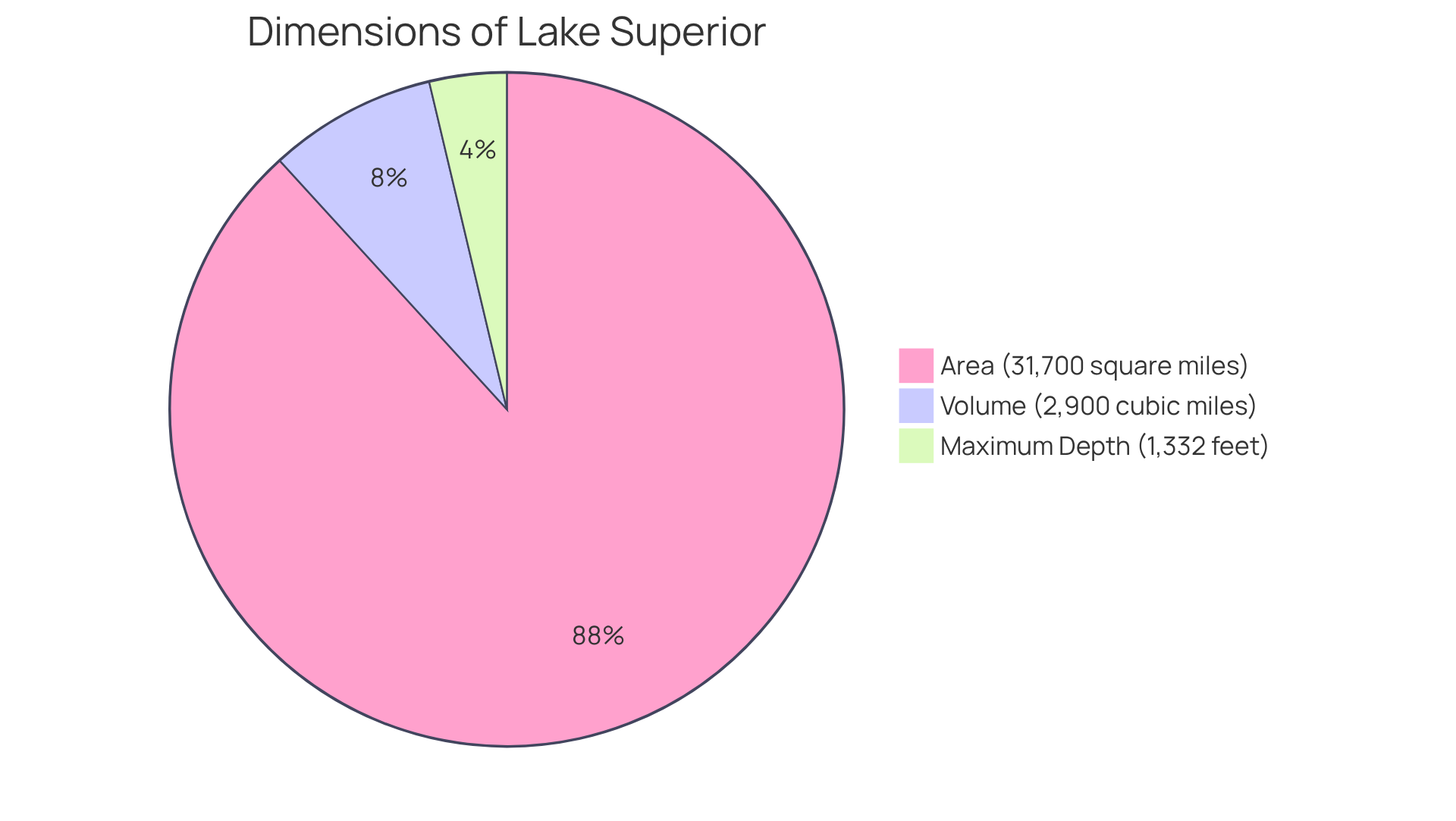
The lake superior dimensions span an impressive 31,700 square miles, establishing it as the largest freshwater body in the world by surface area. With a maximum depth of 1,332 feet, it possesses a staggering total volume of approximately 2,900 cubic miles (12,100 cubic kilometers) of water. This vast volume is crucial for sustaining a rich and diverse ecosystem, while also playing a significant role in shaping local weather patterns and climate. Notably, Lake Superior contains about 10 percent of the planet's surface freshwater, underscoring its global significance.
The Ojibwe term for Lake Superior, 'Kitchigami,' meaning 'great body of water,' reflects its profound cultural importance. The lake superior dimensions are pivotal within the Great Lakes system, influencing interactions with surrounding environments. For instance, its substantial water volume aids in temperature regulation, fostering a unique microclimate that affects both flora and fauna in the region.
Furthermore, Lake Superior is recognized as one of the fastest-warming bodies of water worldwide, highlighting the ecological challenges it faces. Geographers emphasize that these characteristics are essential for understanding the ecological dynamics of this expansive freshwater body and its significance in the context of climate change. Historical references, such as the French settlers designating it 'Le Lac Haut' in the 17th century, further enrich the narrative of this remarkable body of water.
Understand the Ecological Importance of Lake Superior's Dimensions
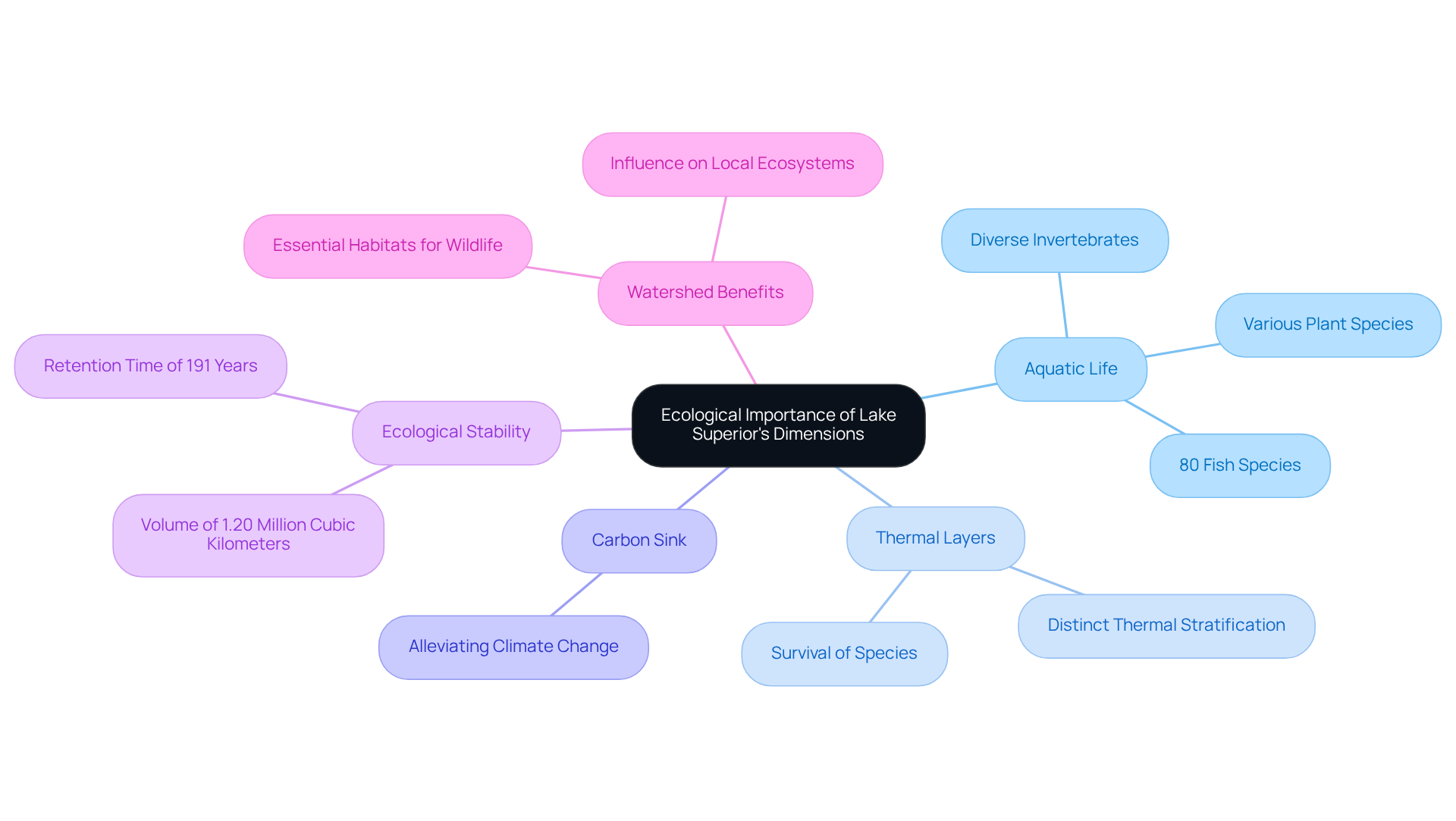
The lake superior dimensions, along with the dimensions of the Great Lakes, are vital to their ecological well-being, supporting a rich tapestry of aquatic life that includes over 80 fish species, diverse invertebrates, and various plant species. The considerable depth of the lake fosters distinct thermal layers, which are crucial for the survival of different species throughout the seasons.
Furthermore, its vast region allows this large body of water to serve as an important carbon sink, significantly contributing to alleviating the impacts of climate change. With a retention time of 191 years, Lake Superior demonstrates ecological stability, and its lake superior dimensions, which include a volume of 1.20 million cubic kilometers, underscore its importance as a freshwater resource, containing 10 percent of the world's available surface freshwater.
The surrounding watershed benefits from the lake superior dimensions, which influence local ecosystems and provide essential habitats for wildlife. Understanding these intricate ecological connections is essential for promoting sustainable practices and safeguarding this invaluable natural resource.
Conclusion
Lake Superior stands out not only as the largest freshwater body by surface area but also as a vital ecological resource that shapes the environment around it. Its impressive dimensions, including a maximum depth of 1,332 feet and a vast area of 31,700 square miles, play a crucial role in supporting diverse aquatic life and maintaining the ecological balance of the region. The lake's unique hydrological characteristics, coupled with its cultural significance to the Anishinaabe community, underscore the importance of preserving this natural treasure.
The article delves into the intricate interplay between Lake Superior's dimensions and its ecological impact. It emphasizes the lake's role as a carbon sink, its retention time of 191 years, and the various fish species that inhabit its cold, clear waters. Additionally, the lake's substantial volume influences local weather patterns and climate, demonstrating its significance not just locally but globally as well. Understanding these factors is essential for implementing effective conservation strategies and ensuring the lake's health for future generations.
In light of the challenges posed by climate change and environmental degradation, recognizing the ecological importance of Lake Superior's dimensions becomes increasingly critical. It is imperative to advocate for sustainable practices that protect this invaluable resource, ensuring that it continues to support a rich tapestry of life and serves as a symbol of natural beauty and cultural heritage. Engaging with and educating others about Lake Superior's significance can foster a collective responsibility to safeguard its future.
Frequently Asked Questions
What are the dimensions of Lake Superior?
Lake Superior spans approximately 31,700 square miles (82,100 square kilometers), making it the largest of the Great Lakes by surface area.
How does Lake Superior compare to the other Great Lakes in terms of volume?
Lake Superior has a volume greater than that of all the other Great Lakes combined.
Which major cities are located along the shores of Lake Superior?
Major cities along the shores of Lake Superior include Duluth, Minnesota, and Thunder Bay, Ontario.
What rivers feed into Lake Superior?
Lake Superior is fed by various rivers, including the St. Louis River and the Nipigon River.
How does Lake Superior's water flow to other bodies of water?
Lake Superior flows into Lake Huron through the St. Marys River.
What is the maximum depth of Lake Superior?
The maximum depth of Lake Superior is 1,332 feet (406 meters).
What is the retention time of Lake Superior's waters?
The retention time of Lake Superior's waters is 191 years, indicating a slow turnover of its waters.
How many fish species inhabit Lake Superior?
Lake Superior hosts 52 fish species, which is fewer than any other Great Lake.
Why does Lake Superior have fewer fish species compared to other Great Lakes?
The unique hydrological traits and limited habitats of Lake Superior contribute to its fewer fish species.
What cultural significance does Lake Superior hold?
The Anishinaabe community has inhabited the region surrounding Lake Superior for over 500 years, fostering a profound cultural connection to the water and its resources.
Why is Lake Superior important for conservation efforts?
Lake Superior's intricate aquatic system plays a vital role in preserving the ecological integrity of the area, making it critical for conservation initiatives and maintaining the ecosystem's equilibrium.



