Overview
Wood in the United States stands as a vital resource, distinguished by its fibrous structure and remarkable versatility in applications that span from construction to furniture. This article underscores the multifaceted role of wood in sustainable practices, its substantial economic contributions, and its historical significance. It showcases how wood remains an integral component of American life and industry, reinforcing its cultural and environmental importance.
Introduction
Wood, a fundamental element of American life, transcends its role as merely a building material; it stands as a symbol of craftsmanship, sustainability, and cultural heritage. Its unique characteristics and versatility render it indispensable across various industries, from construction to artisanal crafts. However, with the rising demand for sustainable practices, a pressing question emerges: how can the wood industry balance economic benefits with environmental stewardship? This article explores the multifaceted role of wood in the United States, delving into its historical significance, diverse applications, and the urgent need for sustainable management.
Define Wood: Importance and Characteristics in the U.S.
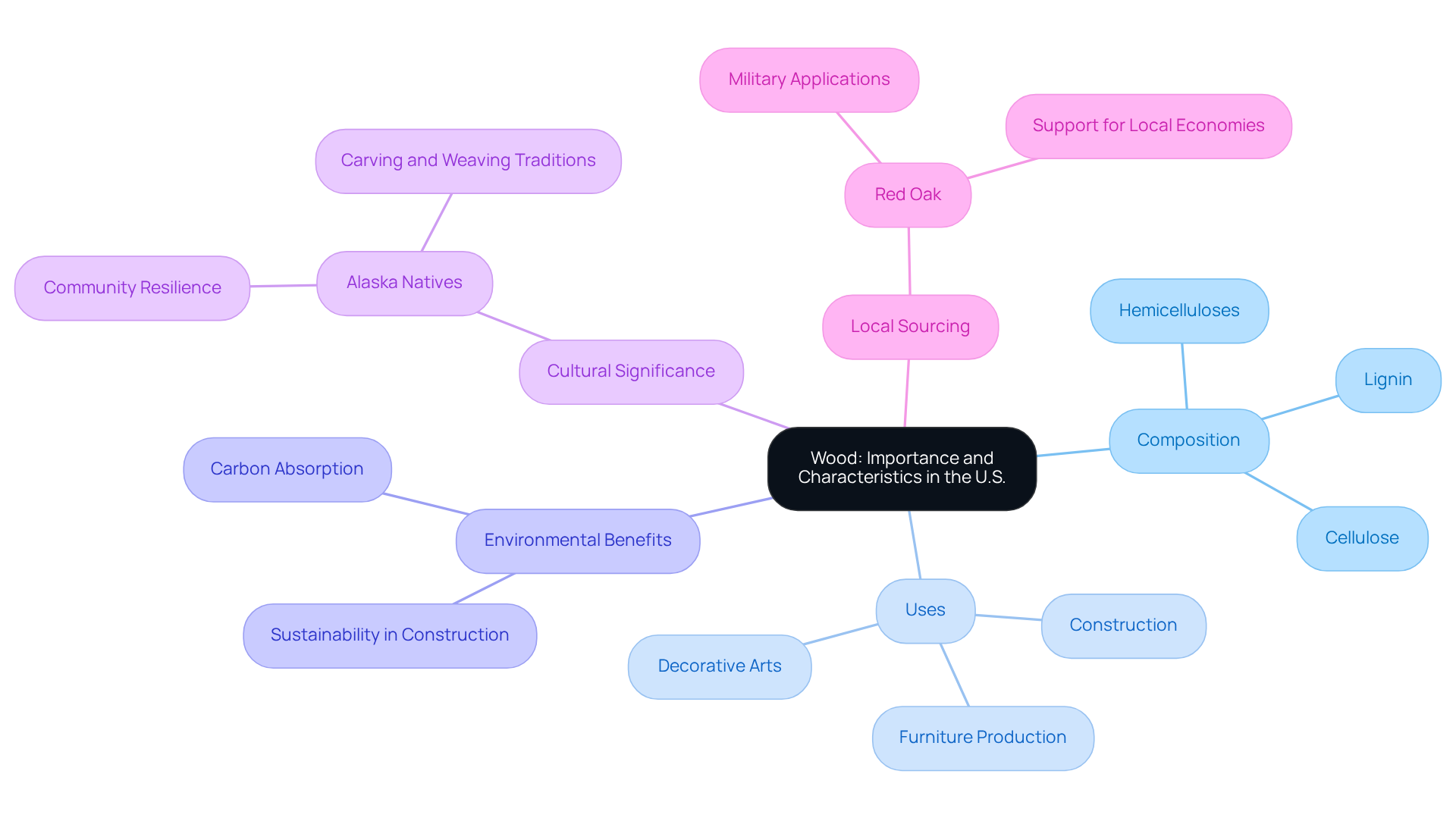
Wood is a fibrous and porous structural tissue derived from trees and other woody plants, primarily composed of cellulose, lignin, and hemicelluloses. In the wood United States, timber is a fundamental building material, valued for its strength, durability, and aesthetic appeal. Its versatility extends beyond construction to furniture production, cabinetry, and decorative arts.
The traits of timber, such as its capacity to absorb and retain carbon, contribute to its role in environmental sustainability, making it a favored option in eco-friendly construction practices. Moreover, the material's cultural significance is profound, integral to various traditional crafts and community identities across the nation.
For instance, the ongoing revitalization of timber products for cultural purposes among Alaska Natives highlights the material's significance in preserving heritage and promoting community resilience. As sectors increasingly emphasize sustainable methods, the utilization of locally sourced hardwoods, such as red oak, not only bolsters local economies but also enhances ecological well-being. This ensures that wood united states continues to be an essential resource in American society.
Explore the Historical Context of Wood Usage in the U.S.
The history of timber utilization in the wood United States dates back to the early colonial period when settlers relied heavily on it for shelter, fuel, and tools. By the 19th century, the lumber industry emerged as a cornerstone of the American economy, with vast forests in the wood United States providing the essential raw materials necessary for expansion and industrialization. The establishment of sawmills and the development of transportation networks facilitated the growth of the lumber trade, making wood in the United States a vital resource for constructing homes, railroads, and infrastructure. Over time, the wood in the United States has remained integral to American culture, symbolizing craftsmanship and sustainability.
In contemporary times, the legacy of wood continues through innovative applications, such as the creation of wooden maps by Pangea Maps. Each map is meticulously hand-sketched over bathymetry ocean charts, showcasing a unique blend of artistry and craftsmanship. These custom designs take around an hour to create, are hand glued, and framed locally, resulting in them being not only decorative pieces but also functional designs that capture significant locations and memories. This artisanal approach to wooden maps highlights Pangea Maps' commitment to crafting unique custom designs that tell your story, making them ideal for corporate gifting. This combination of historical importance and contemporary usefulness highlights the lasting charm of wood in the United States.
Identify Common Types of Wood and Their Applications
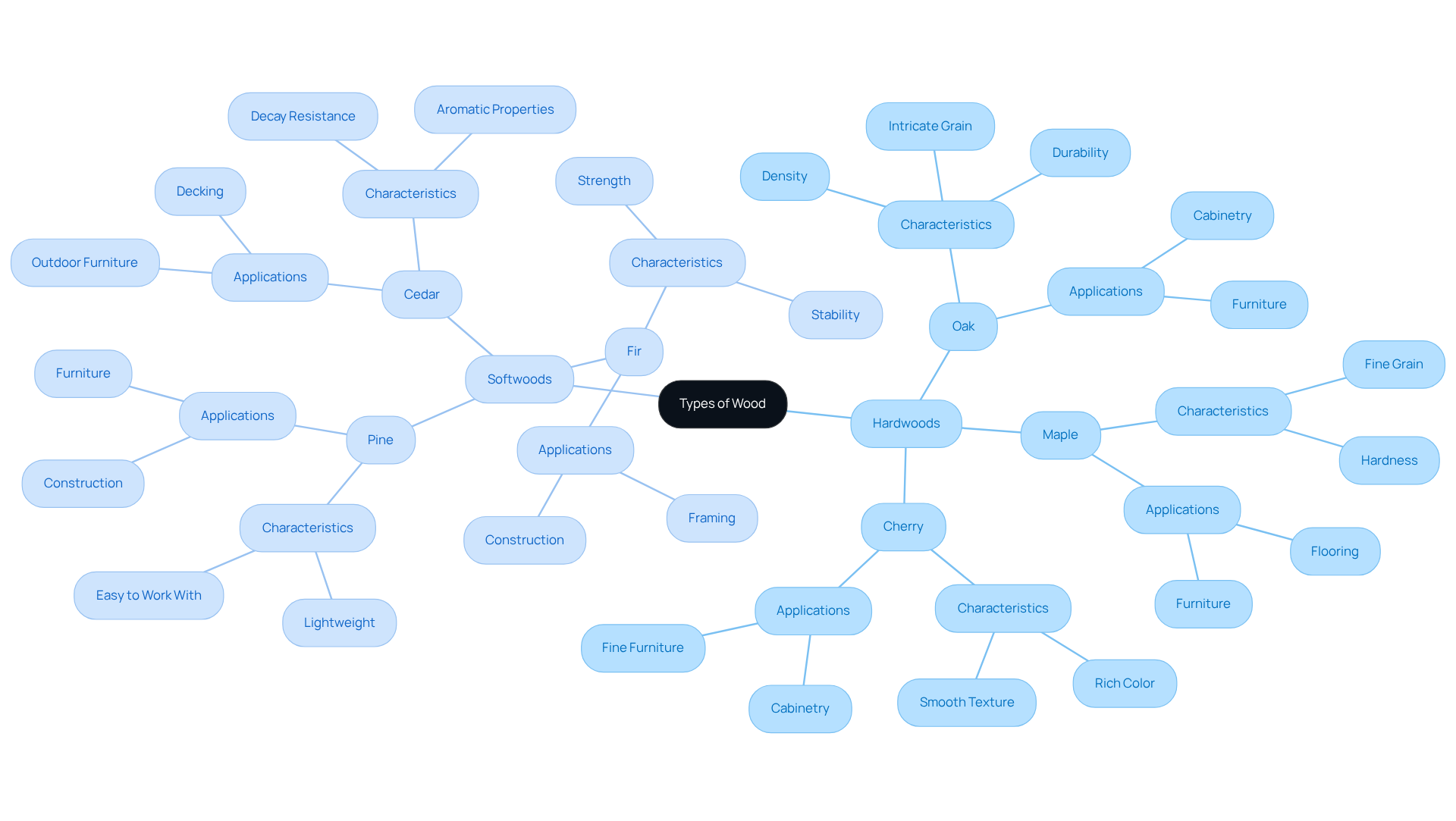
In the wood United States, timber is distinctly classified into two primary categories: hardwoods and softwoods. Hardwoods, such as oak, maple, and cherry, are recognized for their density and durability, making them the preferred choice for furniture and cabinetry. In contrast, softwoods like pine, cedar, and fir are lighter and frequently utilized in construction and framing. Each type of timber exhibits unique characteristics that influence its applications; for example, oak is revered for its strength and intricate grain, while cedar is valued for its remarkable resistance to decay. Understanding these distinctions is essential for selecting the right material for specific projects, whether in construction, furniture crafting, or artistic endeavors.
Assess Environmental and Economic Impacts of Wood in the U.S.
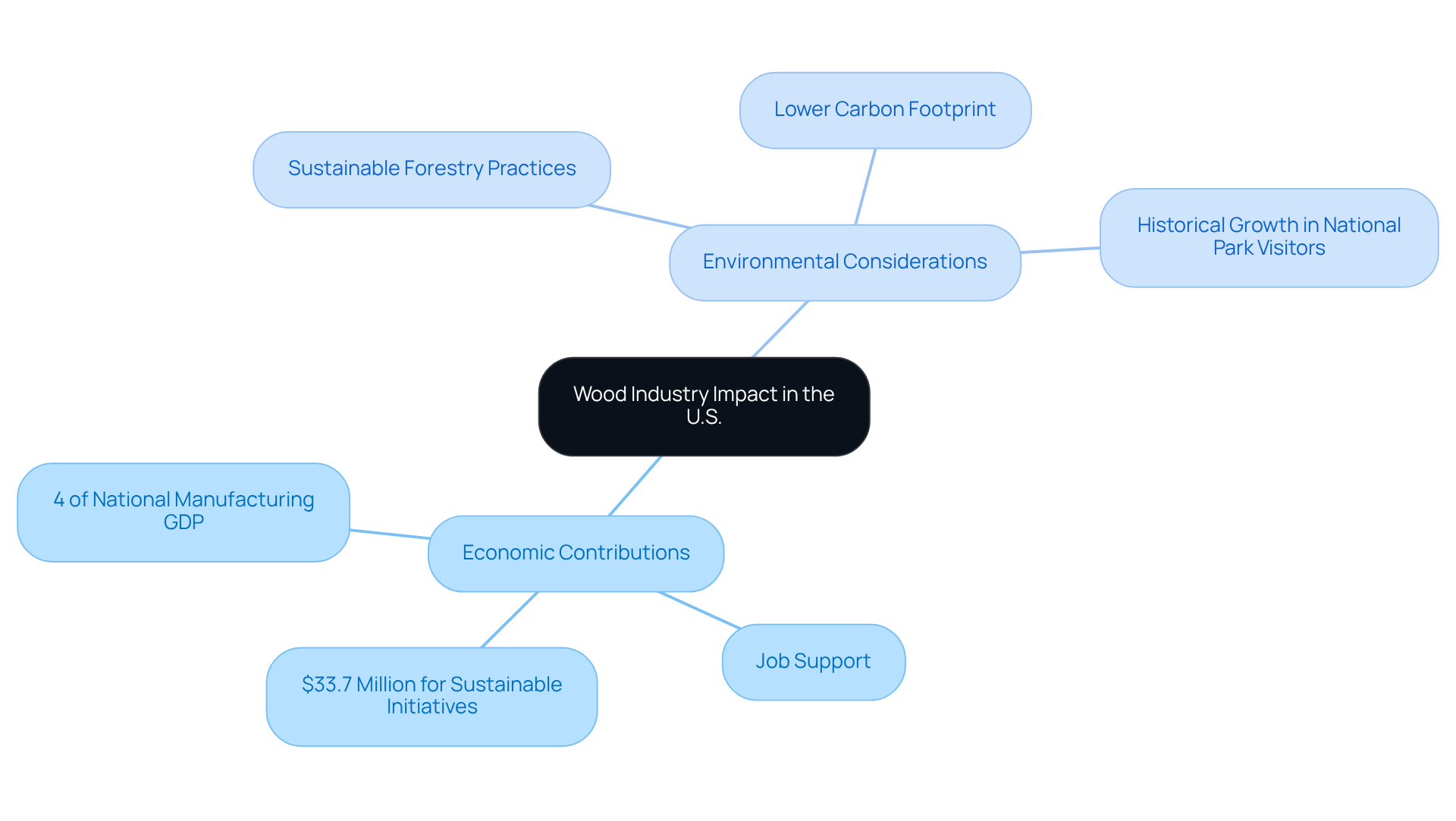
The timber sector, known as the wood industry in the United States, is a vital component of the economy, contributing approximately 4% to the national manufacturing GDP and supporting hundreds of thousands of jobs across various fields. This industry generates billions in revenue, underscoring its economic significance. Notably, $33.7 million has been allocated to support initiatives aimed at enhancing the timber products economy and promoting sustainable forest management.
However, the environmental implications of timber harvesting and production must not be overlooked. Implementing sustainable forestry practices is essential to preserving timber as a renewable resource. Utilizing certified sustainably sourced timber not only combats deforestation but also promotes biodiversity. As Gro Harlem Brundtland articulated, "Sustainable development is the development that meets the needs of the present without compromising the ability of future generations to meet their own needs."
Moreover, timber products generally exhibit a lower carbon footprint compared to alternatives like steel and concrete, positioning them as an environmentally friendly choice for construction and manufacturing. As the demand for eco-friendly methods escalates, the timber sector must adapt to ensure its long-term sustainability and positive impact on both the economy and the environment.
The historical increase in annual visitors to National Parks and National Forests—from over 3 million to nearly 15.5 million in 1939—reflects a growing public interest in sustainability and conservation efforts, further highlighting the necessity for responsible practices within the wood industry in the United States.
Conclusion
Wood stands as a cornerstone of American culture and industry, embodying both practicality and artistry. Its diverse applications—from construction to crafts—highlight its essential role in daily life and the economy. The characteristics of wood, such as its strength, aesthetic appeal, and environmental benefits, underscore its significance as a renewable resource that supports sustainability.
Throughout history, timber has shaped the United States, evolving from a fundamental resource for early settlers to a modern industry that significantly contributes to the economy. The distinction between hardwoods and softwoods illustrates the material's versatility, allowing for tailored applications across various sectors. Furthermore, the commitment to sustainable practices ensures that wood remains an eco-friendly choice, balancing economic growth with environmental stewardship.
As awareness of sustainability grows, embracing responsible wood use becomes increasingly vital. The wood industry not only supports local economies but also plays a crucial role in preserving ecosystems. By choosing sustainably sourced timber and advocating for responsible forestry practices, individuals and businesses can contribute to a future where wood continues to thrive as an invaluable resource in American society.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is wood and what are its main components?
Wood is a fibrous and porous structural tissue derived from trees and other woody plants, primarily composed of cellulose, lignin, and hemicelluloses.
Why is timber considered an important building material in the United States?
Timber is valued for its strength, durability, and aesthetic appeal, making it a fundamental building material in construction.
What are some uses of wood beyond construction?
Beyond construction, wood is used in furniture production, cabinetry, and decorative arts.
How does wood contribute to environmental sustainability?
Wood has the capacity to absorb and retain carbon, which contributes to its role in environmental sustainability and makes it a favored option in eco-friendly construction practices.
What cultural significance does wood have in the U.S.?
Wood is integral to various traditional crafts and community identities across the nation, playing a profound role in cultural heritage.
Can you provide an example of wood's cultural significance?
The revitalization of timber products for cultural purposes among Alaska Natives highlights wood's significance in preserving heritage and promoting community resilience.
How does using locally sourced hardwoods benefit communities?
Utilizing locally sourced hardwoods, such as red oak, bolsters local economies and enhances ecological well-being, ensuring wood remains an essential resource in American society.


